| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Newton’s second law of motion is closely related to Newton’s first law of motion. It mathematically states the cause and effect relationship between force and changes in motion. Newton’s second law of motion is more quantitative and is used extensively to calculate what happens in situations involving a force. Before we can write down Newton’s second law as a simple equation giving the exact relationship of force, mass, and acceleration, we need to sharpen some ideas that have already been mentioned.
First, what do we mean by a change in motion? The answer is that a change in motion is equivalent to a change in velocity. A change in velocity means, by definition, that there is an acceleration . Newton’s first law says that a net external force causes a change in motion; thus, we see that a net external force causes acceleration .
Another question immediately arises. What do we mean by an external force? An intuitive notion of external is correct—an external force acts from outside the system of interest. For example, in [link] (a) the system of interest is the wagon plus the child in it. The two forces exerted by the other children are external forces. An internal force acts between elements of the system. Again looking at [link] (a), the force the child in the wagon exerts to hang onto the wagon is an internal force between elements of the system of interest. Only external forces affect the motion of a system, according to Newton’s first law. (The internal forces actually cancel, as we shall see in the next section.) You must define the boundaries of the system before you can determine which forces are external . Sometimes the system is obvious, whereas other times identifying the boundaries of a system is more subtle. The concept of a system is fundamental to many areas of physics, as is the correct application of Newton’s laws. This concept will be revisited many times on our journey through physics.
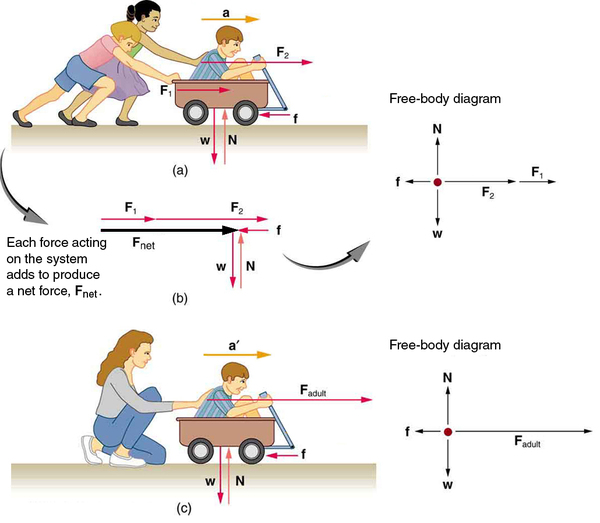
Now, it seems reasonable that acceleration should be directly proportional to and in the same direction as the net (total) external force acting on a system. This assumption has been verified experimentally and is illustrated in [link] . In part (a), a smaller force causes a smaller acceleration than the larger force illustrated in part (c). For completeness, the vertical forces are also shown; they are assumed to cancel since there is no acceleration in the vertical direction. The vertical forces are the weight and the support of the ground , and the horizontal force represents the force of friction. These will be discussed in more detail in later sections. For now, we will define friction as a force that opposes the motion past each other of objects that are touching. [link] (b) shows how vectors representing the external forces add together to produce a net force, .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?