| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
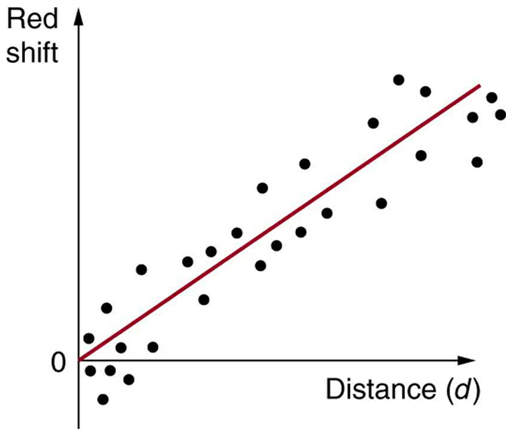
Universal expansion on the scale of galactic clusters (that is, galaxies at smaller distances are not uniformly receding from one another) is an integral part of modern cosmology. For galaxies farther away than about 50 Mly (50 million light years), the expansion is uniform with variations due to local motions of galaxies within clusters. A representative recession velocity can be obtained from the simple formula
where is the distance to the galaxy and is the Hubble constant . The Hubble constant is a central concept in cosmology. Its value is determined by taking the slope of a graph of velocity versus distance, obtained from red shift measurements, such as shown in [link] . We shall use an approximate value of Thus, is an average behavior for all but the closest galaxies. For example, a galaxy 100 Mly away (as determined by its size and brightness) typically moves away from us at a speed of There can be variations in this speed due to so-called local motions or interactions with neighboring galaxies. Conversely, if a galaxy is found to be moving away from us at speed of 100,000 km/s based on its red shift, it is at a distance
or . This last calculation is approximate, because it assumes the expansion rate was the same 5 billion years ago as now. A similar calculation in Hubble’s measurement changed the notion that the universe is in a steady state.
One of the most intriguing developments recently has been the discovery that the expansion of the universe may be faster now than in the past, rather than slowing due to gravity as expected. Various groups have been looking, in particular, at supernovas in moderately distant galaxies (less than 1 Gly) to get improved distance measurements. Those distances are larger than expected for the observed galactic red shifts, implying the expansion was slower when that light was emitted. This has cosmological consequences that are discussed in Dark Matter and Closure . The first results, published in 1999, are only the beginning of emerging data, with astronomy now entering a data-rich era.
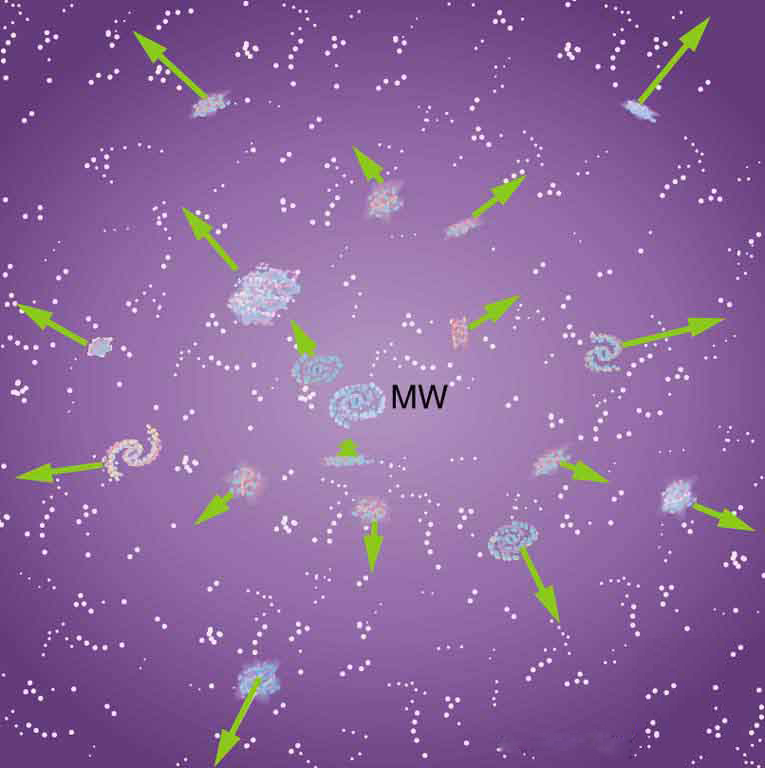
[link] shows how the recession of galaxies looks like the remnants of a gigantic explosion, the famous Big Bang. Extrapolating backward in time, the Big Bang would have occurred between 13 and 15 billion years ago when all matter would have been at a point. Questions instantly arise. What caused the explosion? What happened before the Big Bang? Was there a before, or did time start then? Will the universe expand forever, or will gravity reverse it into a Big Crunch? And is there other evidence of the Big Bang besides the well-documented red shifts?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?