| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Ionizing radiation is widely used to sterilize medical supplies, such as bandages, and consumer products, such as tampons. Worldwide, it is also used to irradiate food, an application that promises to grow in the future. Food irradiation is the treatment of food with ionizing radiation. It is used to reduce pest infestation and to delay spoilage and prevent illness caused by microorganisms. Food irradiation is controversial. Proponents see it as superior to pasteurization, preservatives, and insecticides, supplanting dangerous chemicals with a more effective process. Opponents see its safety as unproven, perhaps leaving worse toxic residues as well as presenting an environmental hazard at treatment sites. In developing countries, food irradiation might increase crop production by 25.0% or more, and reduce food spoilage by a similar amount. It is used chiefly to treat spices and some fruits, and in some countries, red meat, poultry, and vegetables. Over 40 countries have approved food irradiation at some level.
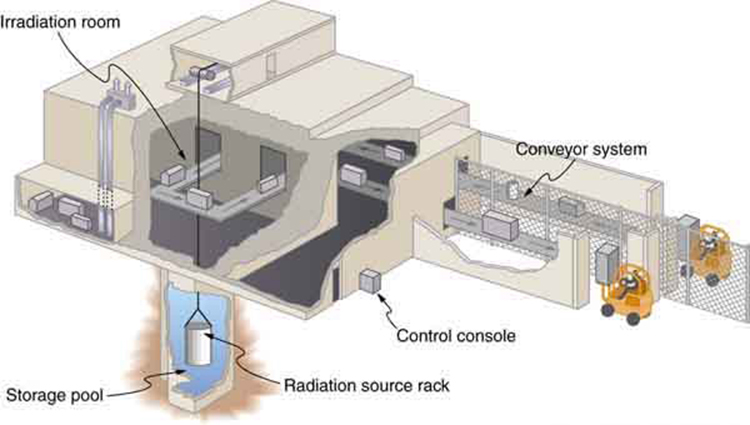
Food irradiation exposes food to large doses of rays, x-rays, or electrons. These photons and electrons induce no nuclear reactions and thus create no residual radioactivity . (Some forms of ionizing radiation, such as neutron irradiation, cause residual radioactivity. These are not used for food irradiation.) The source is usually or , the latter isotope being a major by-product of nuclear power. Cobalt-60 rays average 1.25 MeV, while those of are 0.67 MeV and are less penetrating. X-rays used for food irradiation are created with voltages of up to 5 million volts and, thus, have photon energies up to 5 MeV. Electrons used for food irradiation are accelerated to energies up to 10 MeV. The higher the energy per particle, the more penetrating the radiation is and the more ionization it can create. [link] shows a typical -irradiation plant.
Owing to the fact that food irradiation seeks to destroy organisms such as insects and bacteria, much larger doses than those fatal to humans must be applied. Generally, the simpler the organism, the more radiation it can tolerate. (Cancer cells are a partial exception, because they are rapidly reproducing and, thus, more sensitive.) Current licensing allows up to 1000 Gy to be applied to fresh fruits and vegetables, called a low dose in food irradiation. Such a dose is enough to prevent or reduce the growth of many microorganisms, but about 10,000 Gy is needed to kill salmonella, and even more is needed to kill fungi. Doses greater than 10,000 Gy are considered to be high doses in food irradiation and product sterilization.
The effectiveness of food irradiation varies with the type of food. Spices and many fruits and vegetables have dramatically longer shelf lives. These also show no degradation in taste and no loss of food value or vitamins. If not for the mandatory labeling, such foods subjected to low-level irradiation (up to 1000 Gy) could not be distinguished from untreated foods in quality. However, some foods actually spoil faster after irradiation, particularly those with high water content like lettuce and peaches. Others, such as milk, are given a noticeably unpleasant taste. High-level irradiation produces significant and chemically measurable changes in foods. It produces about a 15% loss of nutrients and a 25% loss of vitamins, as well as some change in taste. Such losses are similar to those that occur in ordinary freezing and cooking.
How does food irradiation work? Ionization produces a random assortment of broken molecules and ions, some with unstable oxygen- or hydrogen-containing molecules known as free radicals . These undergo rapid chemical reactions, producing perhaps four or five thousand different compounds called radiolytic products , some of which make cell function impossible by breaking cell membranes, fracturing DNA, and so on. How safe is the food afterward? Critics argue that the radiolytic products present a lasting hazard, perhaps being carcinogenic. However, the safety of irradiated food is not known precisely. We do know that low-level food irradiation produces no compounds in amounts that can be measured chemically. This is not surprising, since trace amounts of several thousand compounds may be created. We also know that there have been no observable negative short-term effects on consumers. Long-term effects may show up if large number of people consume large quantities of irradiated food, but no effects have appeared due to the small amounts of irradiated food that are consumed regularly. The case for safety is supported by testing of animal diets that were irradiated; no transmitted genetic effects have been observed. Food irradiation (at least up to a million rad) has been endorsed by the World Health Organization and the UN Food and Agricultural Organization. Finally, the hazard to consumers, if it exists, must be weighed against the benefits in food production and preservation. It must also be weighed against the very real hazards of existing insecticides and food preservatives.
Does food irradiation leave the food radioactive? To what extent is the food altered chemically for low and high doses in food irradiation?
Compare a low dose of radiation to a human with a low dose of radiation used in food treatment.
Suppose one food irradiation plant uses a source while another uses an equal activity of . Assuming equal fractions of the rays from the sources are absorbed, why is more time needed to get the same dose using the source?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?