| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
High-resolution measurements of atomic and molecular spectra show that the spectral lines are even more complex than they first appear. In this section, we will see that this complexity has yielded important new information about electrons and their orbits in atoms.
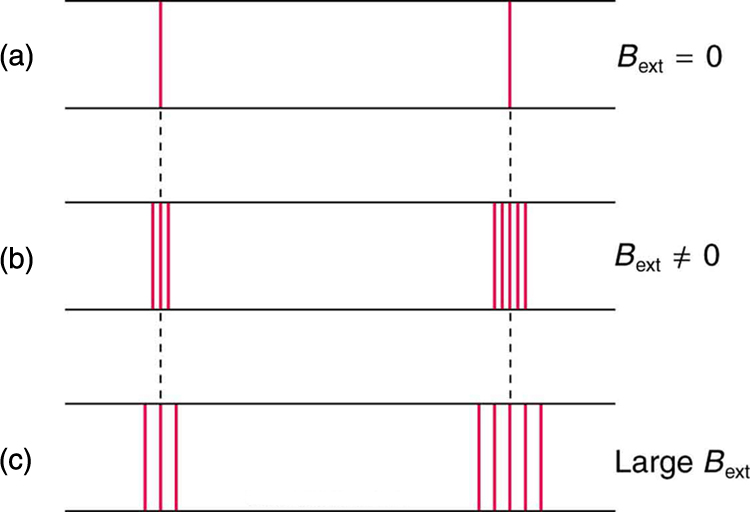
In order to explore the substructure of atoms (and knowing that magnetic fields affect moving charges), the Dutch physicist Hendrik Lorentz (1853–1930) suggested that his student Pieter Zeeman (1865–1943) study how spectra might be affected by magnetic fields. What they found became known as the Zeeman effect , which involved spectral lines being split into two or more separate emission lines by an external magnetic field, as shown in [link] . For their discoveries, Zeeman and Lorentz shared the 1902 Nobel Prize in Physics.
Zeeman splitting is complex. Some lines split into three lines, some into five, and so on. But one general feature is that the amount the split lines are separated is proportional to the applied field strength, indicating an interaction with a moving charge. The splitting means that the quantized energy of an orbit is affected by an external magnetic field, causing the orbit to have several discrete energies instead of one. Even without an external magnetic field, very precise measurements showed that spectral lines are doublets (split into two), apparently by magnetic fields within the atom itself.
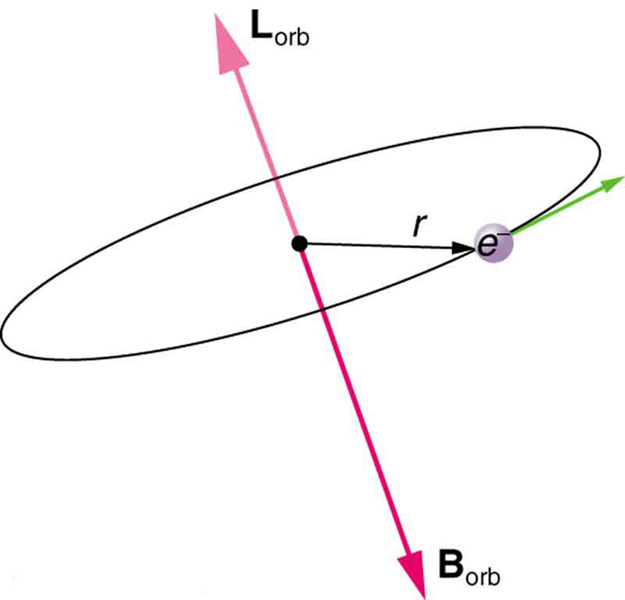
Bohr’s theory of circular orbits is useful for visualizing how an electron’s orbit is affected by a magnetic field. The circular orbit forms a current loop, which creates a magnetic field of its own, as seen in [link] . Note that the orbital magnetic field and the orbital angular momentum are along the same line. The external magnetic field and the orbital magnetic field interact; a torque is exerted to align them. A torque rotating a system through some angle does work so that there is energy associated with this interaction. Thus, orbits at different angles to the external magnetic field have different energies. What is remarkable is that the energies are quantized—the magnetic field splits the spectral lines into several discrete lines that have different energies. This means that only certain angles are allowed between the orbital angular momentum and the external field, as seen in [link] .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?