| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Calculate the rest energy of a 1.00-g mass.
Strategy
One gram is a small mass—less than half the mass of a penny. We can multiply this mass, in SI units, by the speed of light squared to find the equivalent rest energy.
Solution
Noting that , we see the rest mass energy is
Discussion
This is an enormous amount of energy for a 1.00-g mass. We do not notice this energy, because it is generally not available. Rest energy is large because the speed of light is a large number and is a very large number, so that is huge for any macroscopic mass. The rest mass energy for 1.00 g is about twice the energy released by the Hiroshima atomic bomb and about 10,000 times the kinetic energy of a large aircraft carrier. If a way can be found to convert rest mass energy into some other form (and all forms of energy can be converted into one another), then huge amounts of energy can be obtained from the destruction of mass.
Today, the practical applications of the conversion of mass into another form of energy , such as in nuclear weapons and nuclear power plants, are well known. But examples also existed when Einstein first proposed the correct form of relativistic energy, and he did describe some of them. Nuclear radiation had been discovered in the previous decade, and it had been a mystery as to where its energy originated. The explanation was that, in certain nuclear processes, a small amount of mass is destroyed and energy is released and carried by nuclear radiation. But the amount of mass destroyed is so small that it is difficult to detect that any is missing. Although Einstein proposed this as the source of energy in the radioactive salts then being studied, it was many years before there was broad recognition that mass could be and, in fact, commonly is converted to energy. (See [link] .)
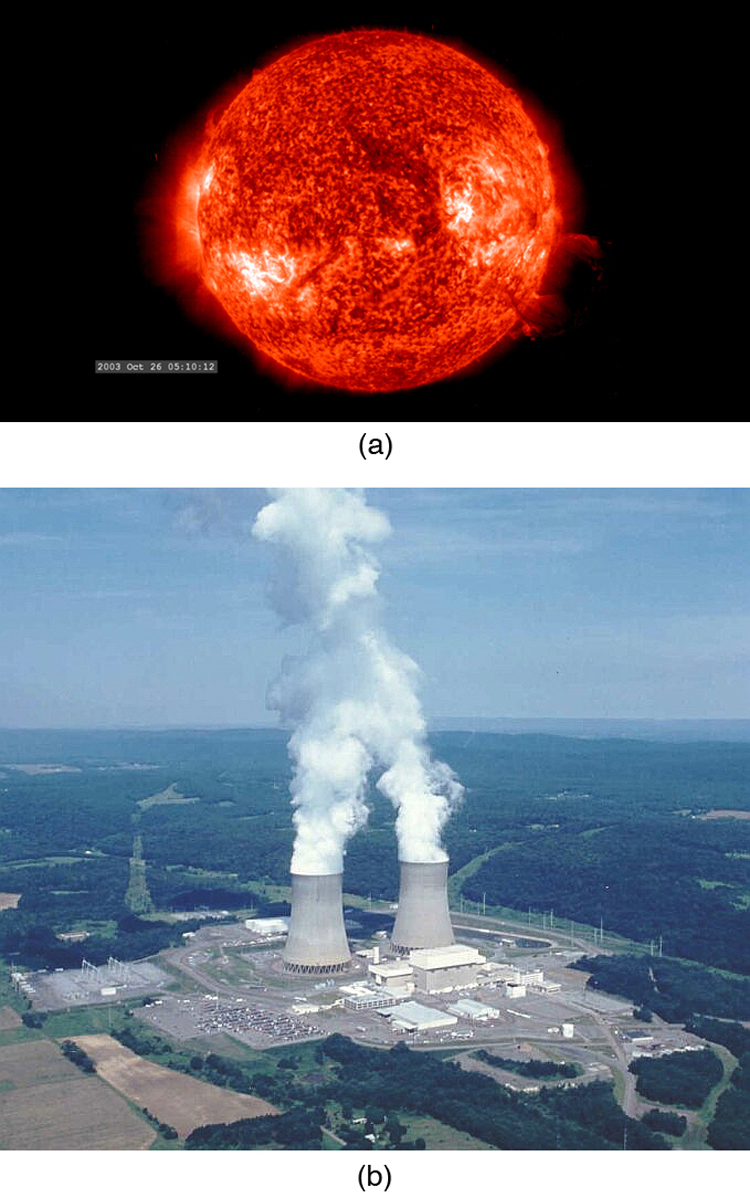
Because of the relationship of rest energy to mass, we now consider mass to be a form of energy rather than something separate. There had not even been a hint of this prior to Einstein’s work. Such conversion is now known to be the source of the Sun’s energy, the energy of nuclear decay, and even the source of energy keeping Earth’s interior hot.
What happens to energy stored in an object at rest, such as the energy put into a battery by charging it, or the energy stored in a toy gun’s compressed spring? The energy input becomes part of the total energy of the object and, thus, increases its rest mass. All stored and potential energy becomes mass in a system. Why is it we don’t ordinarily notice this? In fact, conservation of mass (meaning total mass is constant) was one of the great laws verified by 19th-century science. Why was it not noticed to be incorrect? The following example helps answer these questions.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?