| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |

If you’ve ever seen a kayak move down a fast-moving river, you know that remaining in the same place would be hard. The river current pulls the kayak along. Pushing the oars back against the water can move the kayak forward in the water, but that only accounts for part of the velocity. The kayak’s motion is an example of classical addition of velocities. In classical physics, velocities add as vectors. The kayak’s velocity is the vector sum of its velocity relative to the water and the water’s velocity relative to the riverbank.
For simplicity, we restrict our consideration of velocity addition to one-dimensional motion. Classically, velocities add like regular numbers in one-dimensional motion. (See [link] .) Suppose, for example, a girl is riding in a sled at a speed 1.0 m/s relative to an observer. She throws a snowball first forward, then backward at a speed of 1.5 m/s relative to the sled. We denote direction with plus and minus signs in one dimension; in this example, forward is positive. Let be the velocity of the sled relative to the Earth, the velocity of the snowball relative to the Earth-bound observer, and the velocity of the snowball relative to the sled.
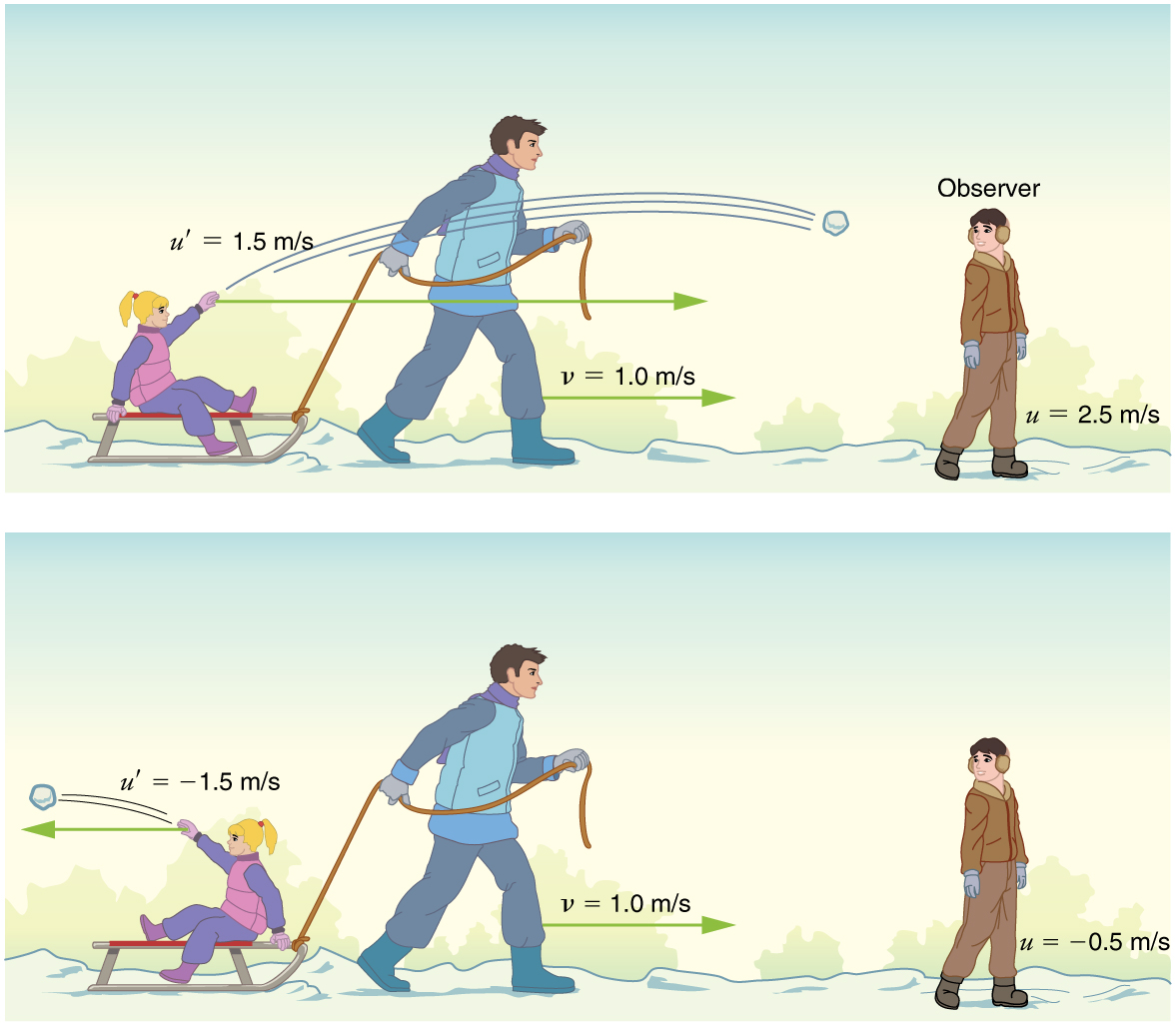
Thus, when the girl throws the snowball forward, . It makes good intuitive sense that the snowball will head towards the Earth-bound observer faster, because it is thrown forward from a moving vehicle. When the girl throws the snowball backward, . The minus sign means the snowball moves away from the Earth-bound observer.
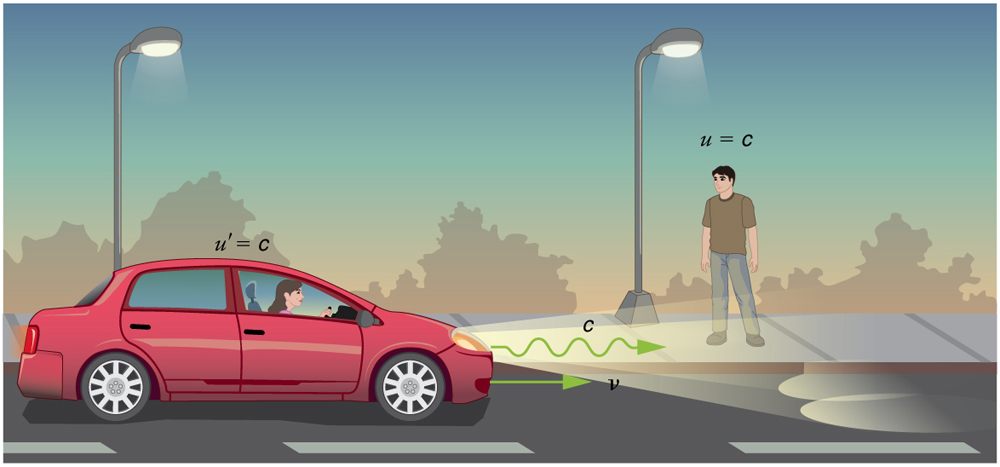
The second postulate of relativity (verified by extensive experimental observation) says that classical velocity addition does not apply to light. Imagine a car traveling at night along a straight road, as in [link] . If classical velocity addition applied to light, then the light from the car’s headlights would approach the observer on the sidewalk at a speed . But we know that light will move away from the car at speed relative to the driver of the car, and light will move towards the observer on the sidewalk at speed , too.


Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?