| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Anyone who has used a microwave oven knows there is energy in electromagnetic waves . Sometimes this energy is obvious, such as in the warmth of the summer sun. Other times it is subtle, such as the unfelt energy of gamma rays, which can destroy living cells.
Electromagnetic waves can bring energy into a system by virtue of their electric and magnetic fields . These fields can exert forces and move charges in the system and, thus, do work on them. If the frequency of the electromagnetic wave is the same as the natural frequencies of the system (such as microwaves at the resonant frequency of water molecules), the transfer of energy is much more efficient.
The behavior of electromagnetic radiation clearly exhibits wave characteristics. But we shall find in later modules that at high frequencies, electromagnetic radiation also exhibits particle characteristics. These particle characteristics will be used to explain more of the properties of the electromagnetic spectrum and to introduce the formal study of modern physics.
Another startling discovery of modern physics is that particles, such as electrons and protons, exhibit wave characteristics. This simultaneous sharing of wave and particle properties for all submicroscopic entities is one of the great symmetries in nature.
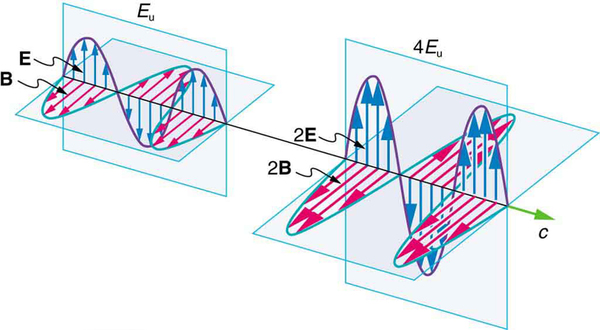
But there is energy in an electromagnetic wave, whether it is absorbed or not. Once created, the fields carry energy away from a source. If absorbed, the field strengths are diminished and anything left travels on. Clearly, the larger the strength of the electric and magnetic fields, the more work they can do and the greater the energy the electromagnetic wave carries.
A wave’s energy is proportional to its amplitude squared ( or ). This is true for waves on guitar strings, for water waves, and for sound waves, where amplitude is proportional to pressure. In electromagnetic waves, the amplitude is the maximum field strength of the electric and magnetic fields. (See [link] .)
Thus the energy carried and the intensity of an electromagnetic wave is proportional to and . In fact, for a continuous sinusoidal electromagnetic wave, the average intensity is given by
where is the speed of light, is the permittivity of free space, and is the maximum electric field strength; intensity, as always, is power per unit area (here in ).
The average intensity of an electromagnetic wave can also be expressed in terms of the magnetic field strength by using the relationship , and the fact that , where is the permeability of free space. Algebraic manipulation produces the relationship

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?