| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
When you use a flash camera, it takes a few seconds to charge the capacitor that powers the flash. The light flash discharges the capacitor in a tiny fraction of a second. Why does charging take longer than discharging? This question and a number of other phenomena that involve charging and discharging capacitors are discussed in this module.
An circuit is one containing a resistor and a capacitor . The capacitor is an electrical component that stores electric charge.
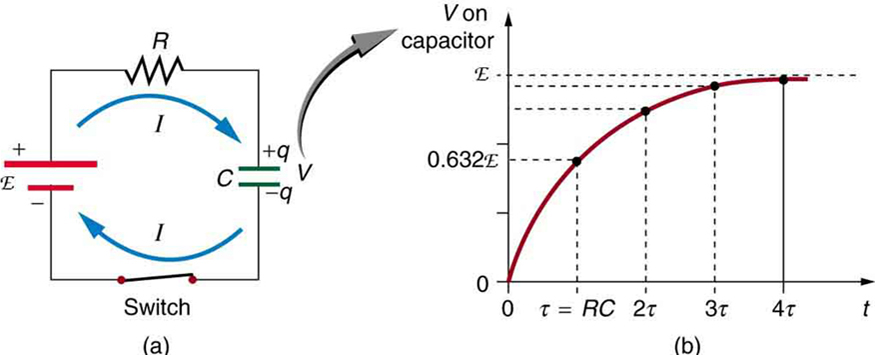
[link] shows a simple circuit that employs a DC (direct current) voltage source. The capacitor is initially uncharged. As soon as the switch is closed, current flows to and from the initially uncharged capacitor. As charge increases on the capacitor plates, there is increasing opposition to the flow of charge by the repulsion of like charges on each plate.
In terms of voltage, this is because voltage across the capacitor is given by , where is the amount of charge stored on each plate and is the capacitance . This voltage opposes the battery, growing from zero to the maximum emf when fully charged. The current thus decreases from its initial value of to zero as the voltage on the capacitor reaches the same value as the emf. When there is no current, there is no drop, and so the voltage on the capacitor must then equal the emf of the voltage source. This can also be explained with Kirchhoff’s second rule (the loop rule), discussed in Kirchhoff’s Rules , which says that the algebraic sum of changes in potential around any closed loop must be zero.
The initial current is , because all of the drop is in the resistance. Therefore, the smaller the resistance, the faster a given capacitor will be charged. Note that the internal resistance of the voltage source is included in , as are the resistances of the capacitor and the connecting wires. In the flash camera scenario above, when the batteries powering the camera begin to wear out, their internal resistance rises, reducing the current and lengthening the time it takes to get ready for the next flash.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?