| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The resistance of an object depends on its shape and the material of which it is composed. The cylindrical resistor in [link] is easy to analyze, and, by so doing, we can gain insight into the resistance of more complicated shapes. As you might expect, the cylinder’s electric resistance is directly proportional to its length , similar to the resistance of a pipe to fluid flow. The longer the cylinder, the more collisions charges will make with its atoms. The greater the diameter of the cylinder, the more current it can carry (again similar to the flow of fluid through a pipe). In fact, is inversely proportional to the cylinder’s cross-sectional area .
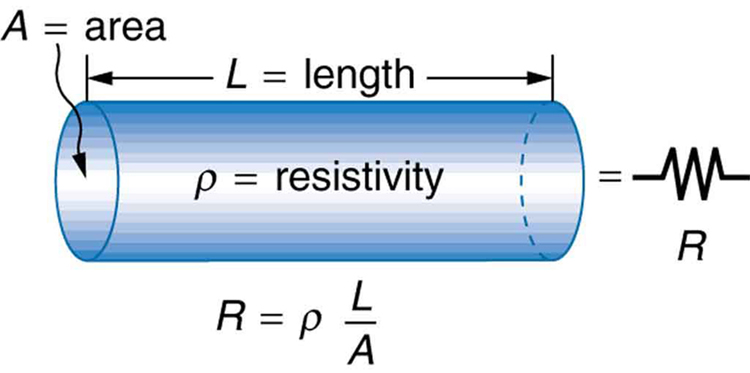
For a given shape, the resistance depends on the material of which the object is composed. Different materials offer different resistance to the flow of charge. We define the resistivity of a substance so that the resistance of an object is directly proportional to . Resistivity is an intrinsic property of a material, independent of its shape or size. The resistance of a uniform cylinder of length , of cross-sectional area , and made of a material with resistivity , is
[link] gives representative values of . The materials listed in the table are separated into categories of conductors, semiconductors, and insulators, based on broad groupings of resistivities. Conductors have the smallest resistivities, and insulators have the largest; semiconductors have intermediate resistivities. Conductors have varying but large free charge densities, whereas most charges in insulators are bound to atoms and are not free to move. Semiconductors are intermediate, having far fewer free charges than conductors, but having properties that make the number of free charges depend strongly on the type and amount of impurities in the semiconductor. These unique properties of semiconductors are put to use in modern electronics, as will be explored in later chapters.
|
|
Resistivity ( ) |
|---|---|
| Conductors | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Semiconductors Values depend strongly on amounts and types of impurities | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Insulators | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?