| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |

In everyday conversation, to accelerate means to speed up. The accelerator in a car can in fact cause it to speed up. The greater the acceleration , the greater the change in velocity over a given time. The formal definition of acceleration is consistent with these notions, but more inclusive.
Average Acceleration is the rate at which velocity changes ,
where is average acceleration, is velocity, and is time. (The bar over the means average acceleration.)
Because acceleration is velocity in m/s divided by time in s, the SI units for acceleration are , meters per second squared or meters per second per second, which literally means by how many meters per second the velocity changes every second.
Recall that velocity is a vector—it has both magnitude and direction. This means that a change in velocity can be a change in magnitude (or speed), but it can also be a change in direction . For example, if a car turns a corner at constant speed, it is accelerating because its direction is changing. The quicker you turn, the greater the acceleration. So there is an acceleration when velocity changes either in magnitude (an increase or decrease in speed) or in direction, or both.
Acceleration is a vector in the same direction as the change in velocity, . Since velocity is a vector, it can change either in magnitude or in direction. Acceleration is therefore a change in either speed or direction, or both.
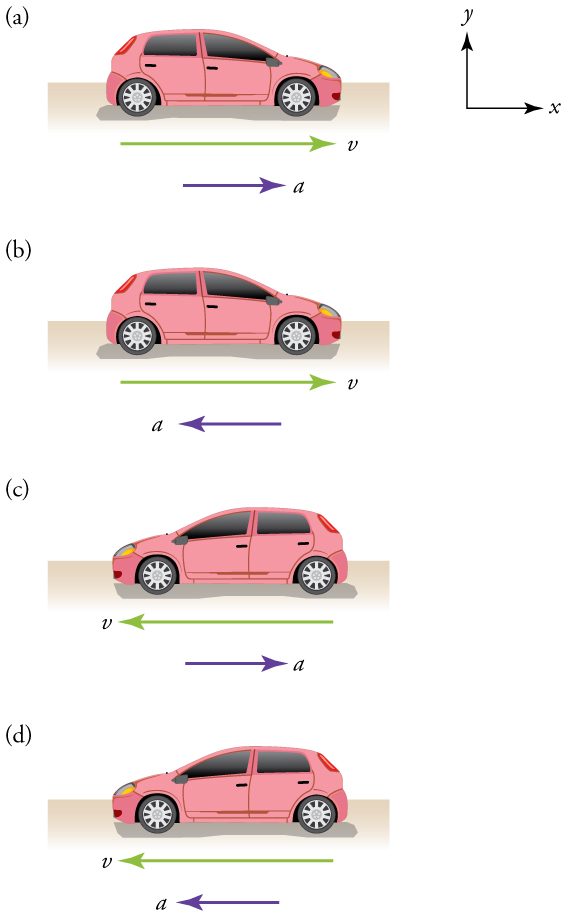
Keep in mind that although acceleration is in the direction of the change in velocity, it is not always in the direction of motion . When an object slows down, its acceleration is opposite to the direction of its motion. This is known as deceleration .
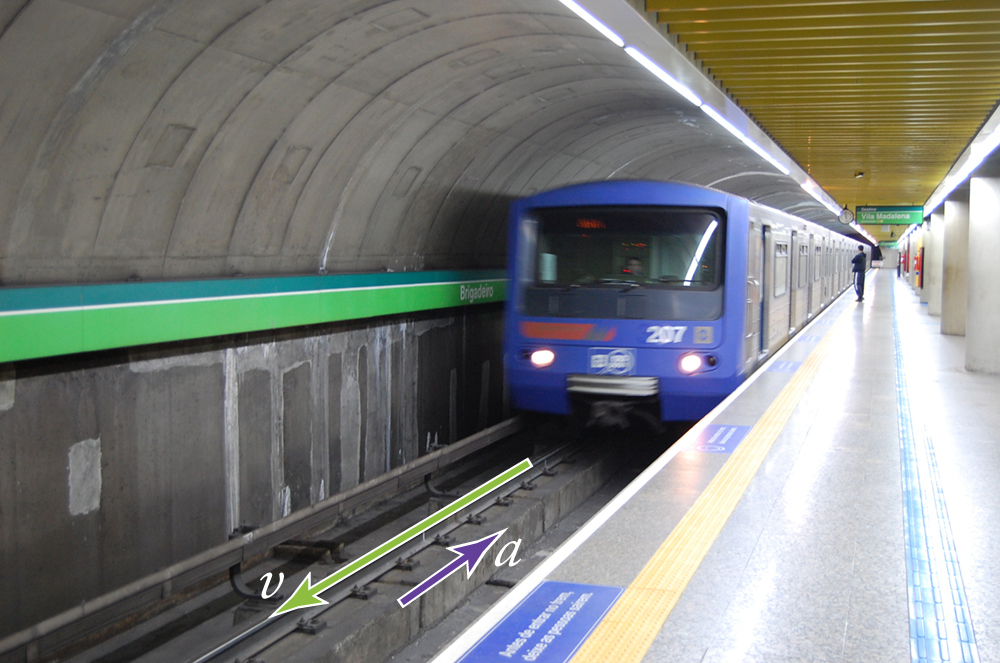

Deceleration always refers to acceleration in the direction opposite to the direction of the velocity. Deceleration always reduces speed. Negative acceleration, however, is acceleration in the negative direction in the chosen coordinate system . Negative acceleration may or may not be deceleration, and deceleration may or may not be considered negative acceleration. For example, consider [link] .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?