| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
We can represent electric potentials (voltages) pictorially, just as we drew pictures to illustrate electric fields. Of course, the two are related. Consider [link] , which shows an isolated positive point charge and its electric field lines. Electric field lines radiate out from a positive charge and terminate on negative charges. While we use blue arrows to represent the magnitude and direction of the electric field, we use green lines to represent places where the electric potential is constant. These are called equipotential lines in two dimensions, or equipotential surfaces in three dimensions. The term equipotential is also used as a noun, referring to an equipotential line or surface. The potential for a point charge is the same anywhere on an imaginary sphere of radius surrounding the charge. This is true since the potential for a point charge is given by and, thus, has the same value at any point that is a given distance from the charge. An equipotential sphere is a circle in the two-dimensional view of [link] . Since the electric field lines point radially away from the charge, they are perpendicular to the equipotential lines.
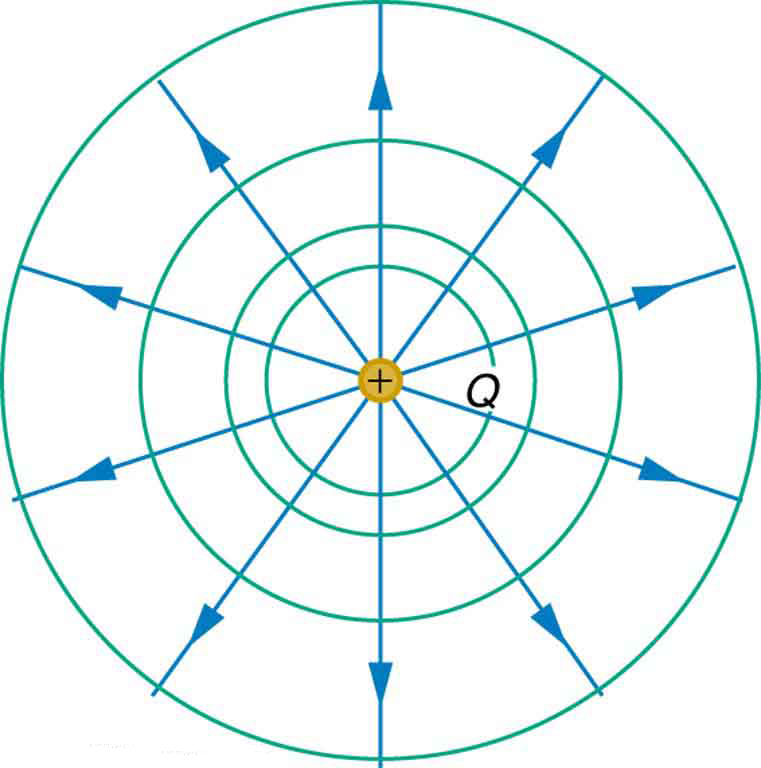
It is important to note that equipotential lines are always perpendicular to electric field lines . No work is required to move a charge along an equipotential, since . Thus the work is
Work is zero if force is perpendicular to motion. Force is in the same direction as , so that motion along an equipotential must be perpendicular to . More precisely, work is related to the electric field by
Note that in the above equation, and symbolize the magnitudes of the electric field strength and force, respectively. Neither nor nor is zero, and so must be 0, meaning must be . In other words, motion along an equipotential is perpendicular to .
One of the rules for static electric fields and conductors is that the electric field must be perpendicular to the surface of any conductor. This implies that a conductor is an equipotential surface in static situations . There can be no voltage difference across the surface of a conductor, or charges will flow. One of the uses of this fact is that a conductor can be fixed at zero volts by connecting it to the earth with a good conductor—a process called grounding . Grounding can be a useful safety tool. For example, grounding the metal case of an electrical appliance ensures that it is at zero volts relative to the earth.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?