| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Bowling pins are sent flying and spinning when hit by a bowling ball—angular momentum as well as linear momentum and energy have been imparted to the pins. (See [link] ). Many collisions involve angular momentum. Cars, for example, may spin and collide on ice or a wet surface. Baseball pitchers throw curves by putting spin on the baseball. A tennis player can put a lot of top spin on the tennis ball which causes it to dive down onto the court once it crosses the net. We now take a brief look at what happens when objects that can rotate collide.
Consider the relatively simple collision shown in [link] , in which a disk strikes and adheres to an initially motionless stick nailed at one end to a frictionless surface. After the collision, the two rotate about the nail. There is an unbalanced external force on the system at the nail. This force exerts no torque because its lever arm is zero. Angular momentum is therefore conserved in the collision. Kinetic energy is not conserved, because the collision is inelastic. It is possible that momentum is not conserved either because the force at the nail may have a component in the direction of the disk’s initial velocity. Let us examine a case of rotation in a collision in [link] .

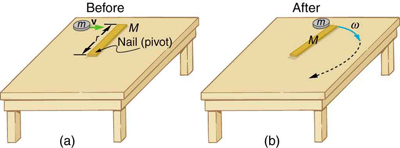
Suppose the disk in [link] has a mass of 50.0 g and an initial velocity of 30.0 m/s when it strikes the stick that is 1.20 m long and 2.00 kg.
(a) What is the angular velocity of the two after the collision?
(b) What is the kinetic energy before and after the collision?
(c) What is the total linear momentum before and after the collision?
Strategy for (a)
We can answer the first question using conservation of angular momentum as noted. Because angular momentum is , we can solve for angular velocity.
Solution for (a)
Conservation of angular momentum states
where primed quantities stand for conditions after the collision and both momenta are calculated relative to the pivot point. The initial angular momentum of the system of stick-disk is that of the disk just before it strikes the stick. That is,
where is the moment of inertia of the disk and is its angular velocity around the pivot point. Now, (taking the disk to be approximately a point mass) and , so that
After the collision,
It is that we wish to find. Conservation of angular momentum gives
Rearranging the equation yields
where is the moment of inertia of the stick and disk stuck together, which is the sum of their individual moments of inertia about the nail. [link] gives the formula for a rod rotating around one end to be . Thus,

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?