| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Johannes Kepler analyzed Tycho Brahe’s data and proposed three basic laws that govern planetary motion of solar system. The importance of his laws lies in the fact that he gave these laws long before Newton’s laws of motion and gravitation. The brilliance of the Kepler’s laws is remarkable as his laws are consistent with Newton’s laws and conservation laws.
Kepler proposed three laws for planetary motion. First law tells about the nature of orbit. Second law tells about the speed of the planet. Third law tells about time period of revolution.
The first law (law of orbits) is stated as :
This law describes the trajectory of a planet, which is an ellipse – not a circle. We have seen that application of mechanics also provides for elliptical trajectory. Only additional thing is that solution of mechanics yields possibilities of other trajectories as well. Thus, we can conclude that Kepler’s law of orbit is consistent with Newtonian mechanics.
We should, however, note that eccentricity of elliptical path is very small for Earth (0.0167) and large for Mercury (0.206) and Pluto (0.25).
Law of velocities is a statement of comparative velocities of planets at different positions along the elliptical path.
This law states that the speed of the planet is not constant as generally might have been conjectured from uniform circular motion. Rather it varies along its path. A given area drawn to the focus is wider when it is closer to Sun. From the figure, it is clear that planet covers smaller arc length when it is away and a larger arc length when it is closer for a given orbital area drawn from the position of Sun. It means that speed of the planet is greater at positions closer to the Sun and smaller at positions away from the Sun.
Equal area swept in equal time
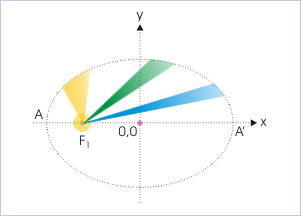
Further on close examination, we find that Kepler’s second law, as a matter of fact, is an statement of the conservations of angular momentum. In order to prove this, let us consider a small orbital area as shown in the figure.
Area swept
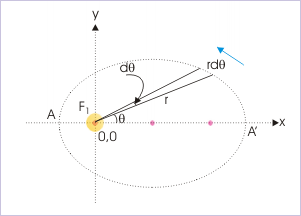
For infinitesimally small area, the “area speed” of the planet (the time rate at which it sweeps orbital area drawn from the Sun) is :
Now, to see the connection of this quantity with angular momentum, let us write the equation of angular momentum :
Substituting this expression in the equation of area – speed, we have :
As no external torque is assumed to exist on the “Sun-planet” system, its angular momentum is conserved. Hence, parameters on the right hand side of the equation i.e. “L” and “m” are constants. This yields that area-speed is constant as proposed by Kepler.
We can interpret the above result other way round also. Kepler’s law says that area-speed of a planet is constant. His observation is based on measured data by Tycho Brahe. It implies that angular momentum of the system remains constant. This means that no external torque applies on the “Sun – planet” system.
The law relates time period of the planet with semi major axis of the elliptical trajectory.
We have already seen in the case of circular trajectory around a larger mass and also in the case of two body system (see Two body system - circular motion )in which each body is moving along two circular trajectories that time period is given by :
The expression of time period for elliptical trajectory is similar except that semi-major axis replaces “r”. We have not proved this in the module, but can be so derived. Squaring each of the side and replacing "r" by "a", we have :
Thus, we conclude the following :
1: The planet follows a elliptical path about Sun.
2: The Sun lies at one of the foci.
3: Gravitational force, centripetal force, linear and angular velocities are variable with the motion.
4: Velocities are maximum at perihelion and minimum at aphelion.
5: Although angular velocity is variable, the angular momentum of the system is conserved.
6: The expression of total mechanical energy is same as in the case of circular motion with the exception that semi major axis, “a”, replaces radius, “r”.
7: The expression of time period is same as in the case of circular motion with the exception that semi major axis, “a”, replaces radius, “r”.
8: Kepler’s three laws are consistent with Newtonian mechanics.
Author wishes to place special thanks to Mr. Mark Prange, Port Isabel, Texas, USA and David F Shively for their valuable editorial suggestions on the subject discussed in this module.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physics for k-12' conversation and receive update notifications?