| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Focal points ( and ) lie on semi major axis at a distance from the origin given by
Focal points
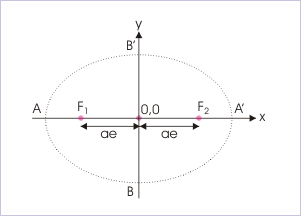
The focus of an ellipse is at a distance “ae” from the center on the semi-major axis. Area of the ellipse is "πab".
Semi latus rectum is equal to distance between one of the foci and ellipse as measured along a line perpendicular to the major axis. This is shown in the figure.
Semi latus rectum
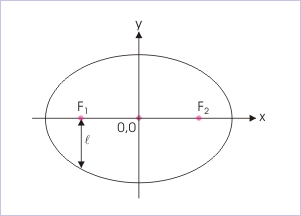
For an ellipse, Semi latus rectum has the expression in terms of “a” and “b” as :
We can also express the same involving eccentricity as :
The solar system consists of Sun and its planets. The reason they are together is gravitation. The mass of the planet is relatively small with respect to Sun. For example, Earth compares about times smaller in mass with respect to Sun :
Mass of Earth :
Mass of Sun :
The planetary motion, therefore, fits nicely with elliptical solution obtained from consideration of mechanics. Sun, being many times heavier, appears to be at the “center of mass” of the system i.e. at one of the foci, while planets revolve around it in elliptical orbits of different eccentricities.
Polar coordinates generally suite geometry of ellipse. The figure shows the polar coordinates of a point on the ellipse. It is important to note that one of foci serves as the origin of polar coordinates, whereas the other focus lies on the negative x-axis. For this reason orientation of x-axis is reversed in the figure. The angle is measured anti-clockwise and the equation of ellipse in polar coordinates is :
Equation in polar coordinate
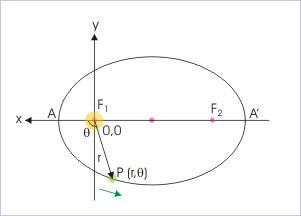
Substituting expression for semi latus rectum
Perihelion position corresponds to minimum distance between Sun and planet. If we consider Sun to be at one focus (say ), then perihelion distance is " " as shown in the figure. We can see that angle θ = 0° for this position.
Minimum and maximum distance
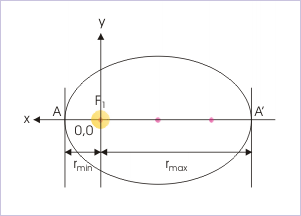
From the figure also, it is clear that minimum distance is equal to “a - ae= a(1-e)”.
Aphelion position corresponds to maximum distance between Sun and planet. If we consider Sun to be at one focus (say ), then perihelion distance is " " as shown in the figure. We can see that angle θ = 180° for this position.
From the figure also, it is clear that maximum distance is equal to “a + ae= a(1+e)”.
We can also prove that the semi-major axis, “a” is arithmetic mean, whereas semi-minor axis, “b”, is geometric mean of “ ” and “ ”.
We can understand planetary motion by recognizing important aspects of motion like force, velocity, angular momentum, energy etc. The first important difference to motion along circular path is that linear distance between Sun and planet is not constant. The immediate implication is that gravitation force is not constant. It is maximum at perihelion position and minimum at aphelion position.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physics for k-12' conversation and receive update notifications?