| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
If “m”,”p” and “ℓ” denote the mass, linear momentum and angular momentum of the particle executing uniform circular motion along a circle of radius “r”, then kinetic energy of the particle is :
From the alternatives given, it is evident that we need to find kinetic energy in terms of linear and angular momentum. Now, the kinetic energy of the particle is expressed as :
The magnitude of linear momentum is given by :
Squaring both sides, we have :
Rearranging,
Combining equations,
Now, the magnitude of angular momentum is given by :
Squaring both sides, we have :
Combining equations,
Hence, options (a) and (c) are correct.
Dimensional formula of angular momentum is :
In order to find dimensional formula, we use the expression of angular momentum :
The dimension of angular momentum is :
Hence, option (c) is correct.
Two point masses “m” and “2m” are attached to a mass-less rod of length “d”, pivoted at point “O” as shown in the figure. The rod is free to move in vertical direction. If “ω” be the angular velocity, then the angular momentum of two particles about the axis of rotation is :
Angular momentum of particle
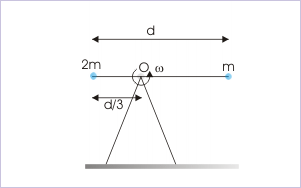
This is a case of rotation. We can solve this problem using either the general expression or specific expression involving moment of inertia. When we use general expression, we should measure moment arm from the axis of rotation.
Since rod is rotating in anticlockwise direction, angular momentum of each particle is positive.
The angular momentum of first particle of mass “m” is :
The angular momentum of second particle of mass “2m” is :
Hence, option (b) is correct.
A particle of mass 100 gram is moving with a constant speed at √2 m/s along a straight line y = x + 2 in "xy" – plane. Then, the magnitude of the angular momentum (in ) about the origin of the coordinate system, if “x” and “y” are in meters, is :
The angular momentum of a particle about a point is defined as :
The magnitude of angular momentum can be evaluated using any of the three methods discussed in the module on the subject. In this case, evaluation of angular momentum involving moment arm is most appropriate. Thus,
We, now, analyze the situation by drawing the figure. The path of the motion is shown. The moment arm i.e. the perpendicular distance of velocity vector from the origin is :
Angular momentum of a particle
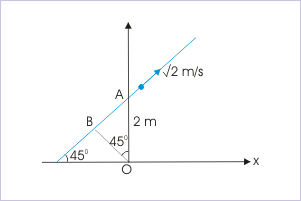
Hence,
Hence, option (b) is correct.
A projectile of mass “m” is projected with a velocity “u”, making and angle “θ” with the horizontal. The angular momentum of the projectile about the point of projection at a given instant “t” during its flight is :
Projectile motion
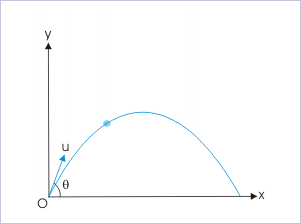
We need to find a general equation for angular momentum for a given time “t”. We observe here that projectile motion is a two dimensional motion for which we can have information in component form. It is, therefore, required to obtain component information for position and the velocity.
Projectile motion
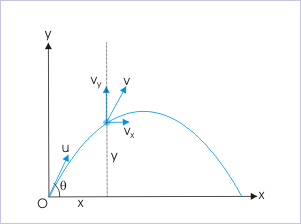
Now, the angular momentum is :
ℓ = |
i
j
k |
| utcosθ utsinθ – 1/2g t*2 0 || u cosθ usinθ – gt 0 |
Hence, option (d) is correct.
1. (a) and (c) 2. (b) 3. (a) 4. (a) and (c) 5. (c) 6. (b)
7. (b) 8. (d)

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physics for k-12' conversation and receive update notifications?