| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The motion of a satellite or space-station is a direct consequence of Earth’s gravity. Once launched in the appropriate orbit, these man-made crafts orbit around Earth without any propulsion. In this module, we shall study basics of satellite motion without going into details of the technology. Also, we shall develop analysis framework of artificial satellite, which can as well be extended to analysis of natural satellite like our moon. For the analysis here, we shall choose a simple framework of “two – body” system, one of which is Earth.
We should be aware that gravity is not the only force of gravitation working on the satellite, particularly if satellite is far off from Earth’s surface. But, Earth being the closest massive body, its gravitational attraction is dominant to the extent of excluding effect of other bodies. For this reason, our analysis of satellite motion as “isolated two body system” is good first approximation.
Mass of artificial satellite is negligible in comparison to that of Earth. The “center of mass” of the “two body system” is about same as the center of Earth. There is possibility of different orbits, which are essentially elliptical with different eccentricity. A satellite close to the surface up to 2000 km describes nearly a circular trajectory. In this module, we shall confine ourselves to the analysis of satellites having circular trajectory only.
Satellites have specific orbital speed to move around Earth, depending on its distance from the center of Earth. The satellite is launched from the surface with the help of a rocket, which parks it in particular orbit with a tangential speed appropriate for that orbit. Since satellite is orbiting along a circular path, there is requirement for the provision of centripetal force, which is always directed towards the center of orbit. This requirement of centripetal force is met by the force of gravity. Hence,
Satellite
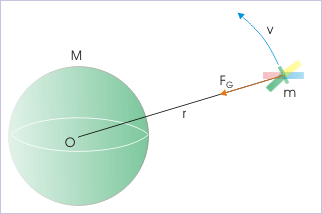
where “M” is Earth’s mass and “r” is linear distance of satellite from the "center of mass" of Earth.
The important thing to realize here are : (i) orbital speed of the satellite is independent of the mass of the satellite (ii) a satellite at a greater distance moves with lesser velocity. As the product “GM” appearing in the numerator of the expression is constant, we can see that
This conclusion is intuitive in the sense that force of gravitation is lesser as we move away from Earth’s surface and the corresponding centripetal force as provided by gravity is smaller. As such, orbital speed is lesser.
This fact has compounding effect on the time period of the satellite. In the first place, a satellite at a greater distance has to travel a longer distance in one revolution than the satellite closer to Earth’s surface. At the same time, orbital speed is lesser as we move away. It is, then, imperative that time period of revolution increases for satellite at greater distance.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physics for k-12' conversation and receive update notifications?