| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
The information presented in this section supports the following AP® learning objectives and science practices:
Matter and photons are waves, implying they are spread out over some distance. What is the position of a particle, such as an electron? Is it at the center of the wave? The answer lies in how you measure the position of an electron. Experiments show that you will find the electron at some definite location, unlike a wave. But if you set up exactly the same situation and measure it again, you will find the electron in a different location, often far outside any experimental uncertainty in your measurement. Repeated measurements will display a statistical distribution of locations that appears wavelike. (See [link] .)
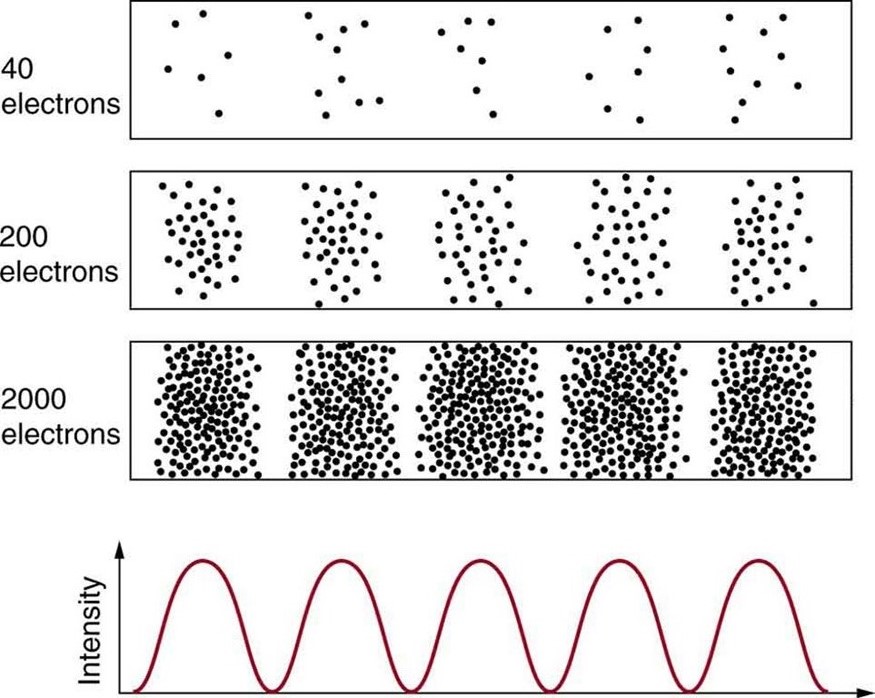
After de Broglie proposed the wave nature of matter, many physicists, including Schrödinger and Heisenberg, explored the consequences. The idea quickly emerged that, because of its wave character, a particle’s trajectory and destination cannot be precisely predicted for each particle individually . However, each particle goes to a definite place (as illustrated in [link] ). After compiling enough data, you get a distribution related to the particle’s wavelength and diffraction pattern. There is a certain probability of finding the particle at a given location, and the overall pattern is called a probability distribution . Those who developed quantum mechanics devised equations that predicted the probability distribution in various circumstances.
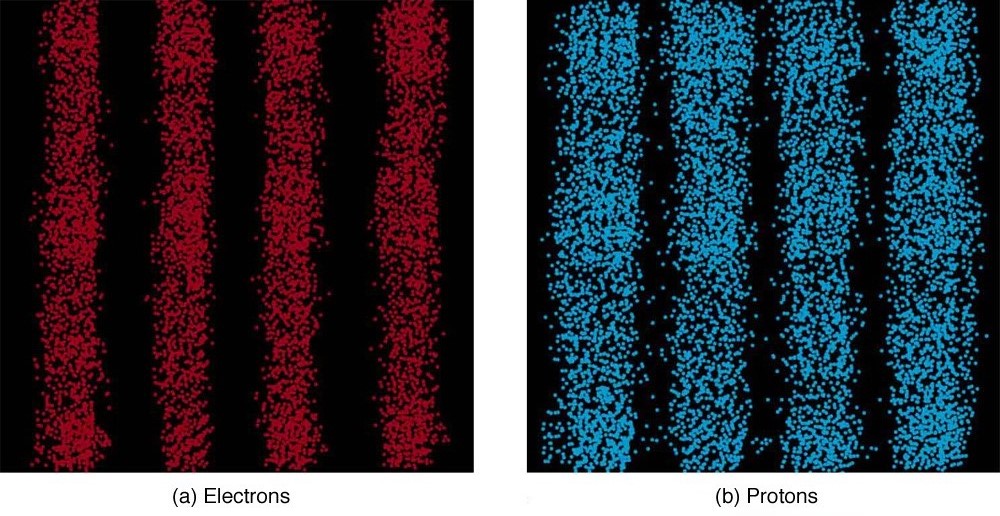
It is somewhat disquieting to think that you cannot predict exactly where an individual particle will go, or even follow it to its destination. Let us explore what happens if we try to follow a particle. Consider the double-slit patterns obtained for electrons and photons in [link] . First, we note that these patterns are identical, following , the equation for double-slit constructive interference developed in Photon Energies and the Electromagnetic Spectrum , where is the slit separation and is the electron or photon wavelength.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?