| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In this section we begin the study of various types of work and forms of energy. We will find that some types of work leave the energy of a system constant, for example, whereas others change the system in some way, such as making it move. We will also develop definitions of important forms of energy, such as the energy of motion.
We know from the study of Newton’s laws in Dynamics: Force and Newton's Laws of Motion that net force causes acceleration. We will see in this section that work done by the net force gives a system energy of motion, and in the process we will also find an expression for the energy of motion.
Let us start by considering the total, or net, work done on a system. Net work is defined to be the sum of work done by all external forces—that is, net work is the work done by the net external force . In equation form, this is where is the angle between the force vector and the displacement vector.
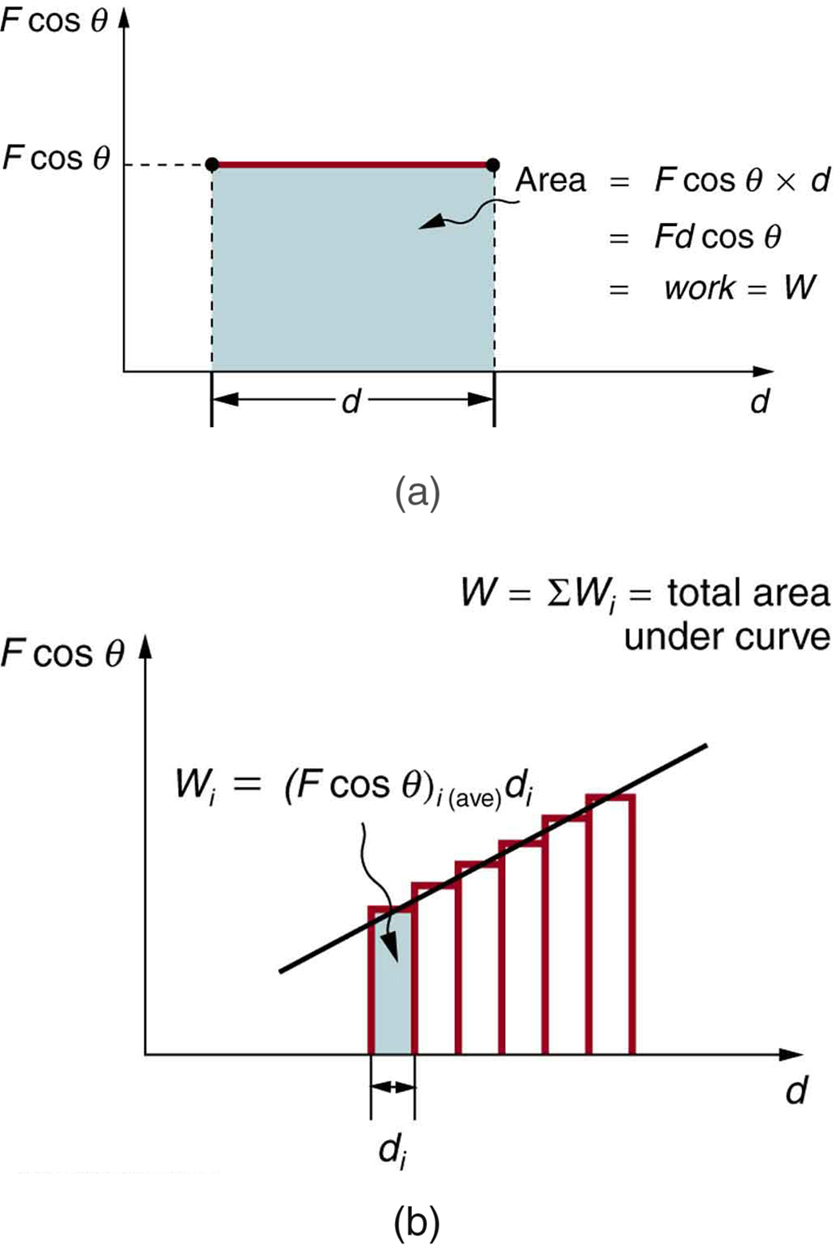
[link] (a) shows a graph of force versus displacement for the component of the force in the direction of the displacement—that is, an vs. graph. In this case, is constant. You can see that the area under the graph is , or the work done. [link] (b) shows a more general process where the force varies. The area under the curve is divided into strips, each having an average force . The work done is for each strip, and the total work done is the sum of the . Thus the total work done is the total area under the curve, a useful property to which we shall refer later.
Consider driving in a car. While moving, you have forward velocity and therefore kinetic energy. When you hit the brakes, they exert a force opposite to your direction of motion (acting through the wheels). The brakes do work on your car and reduce the kinetic energy. Similarly, when you accelerate, the engine (acting through the wheels) exerts a force in the direction of motion. The engine does work on your car, and increases the kinetic energy. Finally, if you go around a corner at a constant speed, you have the same kinetic energy both before and after the corner. The force exerted by the engine was perpendicular to the direction of motion, and therefore did no work and did not change the kinetic energy.
Net work will be simpler to examine if we consider a one-dimensional situation where a force is used to accelerate an object in a direction parallel to its initial velocity. Such a situation occurs for the package on the roller belt conveyor system shown in [link] .
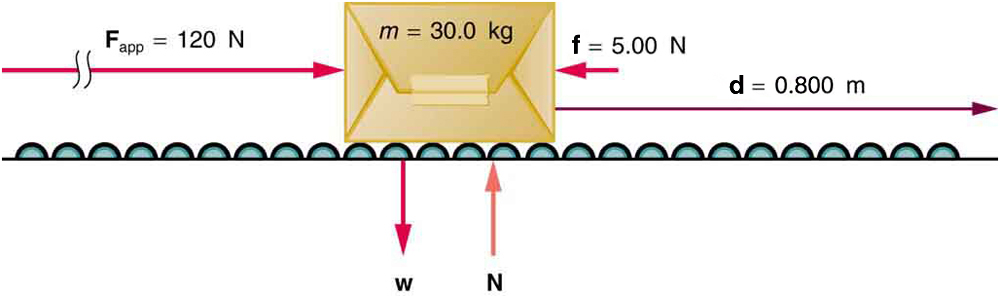
The force of gravity and the normal force acting on the package are perpendicular to the displacement and do no work. Moreover, they are also equal in magnitude and opposite in direction so they cancel in calculating the net force. The net force arises solely from the horizontal applied force and the horizontal friction force . Thus, as expected, the net force is parallel to the displacement, so that and , and the net work is given by

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?