| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |

Lasers today are commonplace. Lasers are used to read bar codes at stores and in libraries, laser shows are staged for entertainment, laser printers produce high-quality images at relatively low cost, and lasers send prodigious numbers of telephone messages through optical fibers. Among other things, lasers are also employed in surveying, weapons guidance, tumor eradication, retinal welding, and for reading music CDs and computer CD-ROMs.
Why do lasers have so many varied applications? The answer is that lasers produce single-wavelength EM radiation that is also very coherent—that is, the emitted photons are in phase. Laser output can, thus, be more precisely manipulated than incoherent mixed-wavelength EM radiation from other sources. The reason laser output is so pure and coherent is based on how it is produced, which in turn depends on a metastable state in the lasing material. Suppose a material had the energy levels shown in [link] . When energy is put into a large collection of these atoms, electrons are raised to all possible levels. Most return to the ground state in less than about , but those in the metastable state linger. This includes those electrons originally excited to the metastable state and those that fell into it from above. It is possible to get a majority of the atoms into the metastable state, a condition called a population inversion .
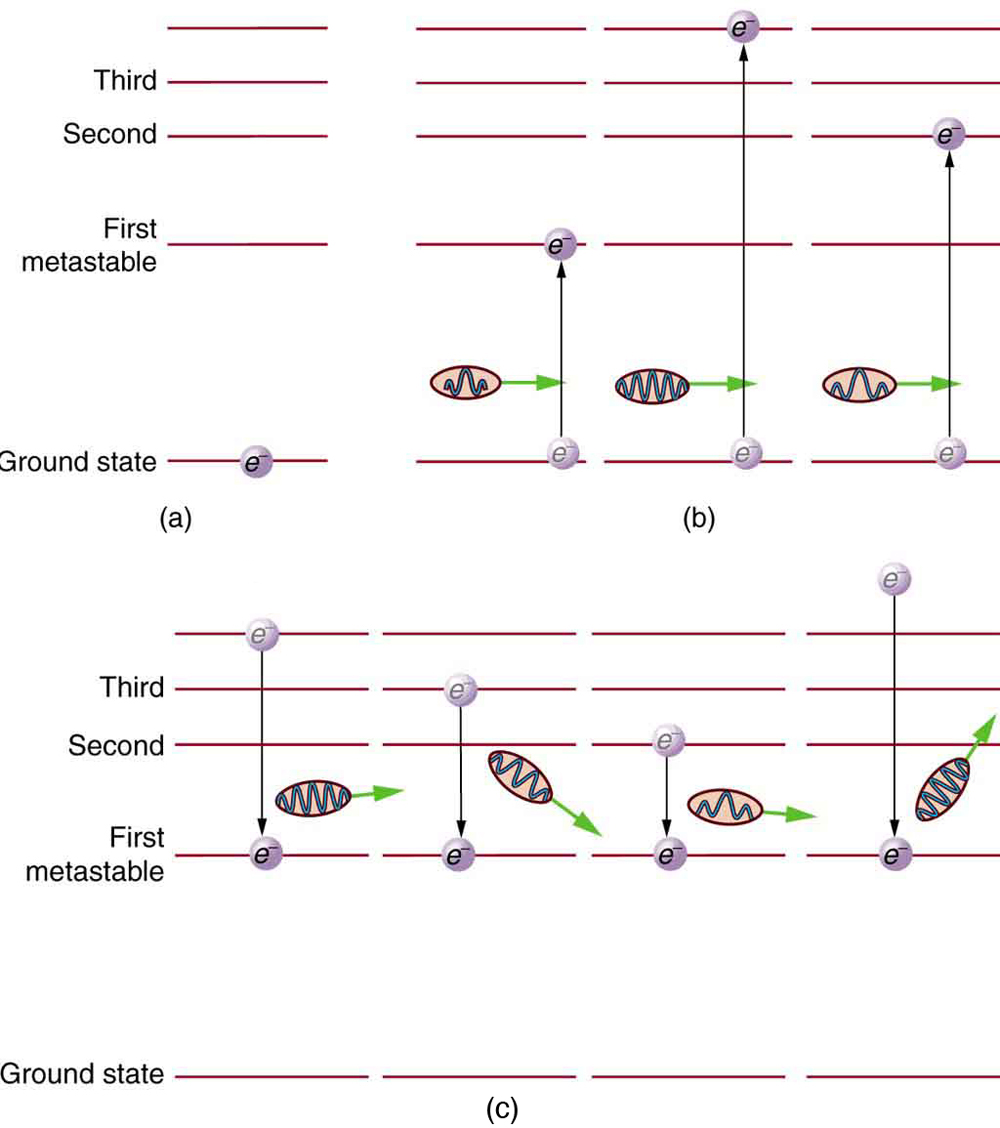
Once a population inversion is achieved, a very interesting thing can happen, as shown in [link] . An electron spontaneously falls from the metastable state, emitting a photon. This photon finds another atom in the metastable state and stimulates it to decay, emitting a second photon of the same wavelength and in phase with the first, and so on. Stimulated emission is the emission of electromagnetic radiation in the form of photons of a given frequency, triggered by photons of the same frequency. For example, an excited atom, with an electron in an energy orbit higher than normal, releases a photon of a specific frequency when the electron drops back to a lower energy orbit. If this photon then strikes another electron in the same high-energy orbit in another atom, another photon of the same frequency is released. The emitted photons and the triggering photons are always in phase, have the same polarization, and travel in the same direction. The probability of absorption of a photon is the same as the probability of stimulated emission, and so a majority of atoms must be in the metastable state to produce energy. Einstein (again Einstein, and back in 1917!) was one of the important contributors to the understanding of stimulated emission of radiation. Among other things, Einstein was the first to realize that stimulated emission and absorption are equally probable. The laser acts as a temporary energy storage device that subsequently produces a massive energy output of single-wavelength, in-phase photons.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?