| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
Classical electrostatics has an important role to play in modern molecular biology. Large molecules such as proteins, nucleic acids, and so on—so important to life—are usually electrically charged. DNA itself is highly charged; it is the electrostatic force that not only holds the molecule together but gives the molecule structure and strength. [link] is a schematic of the DNA double helix.
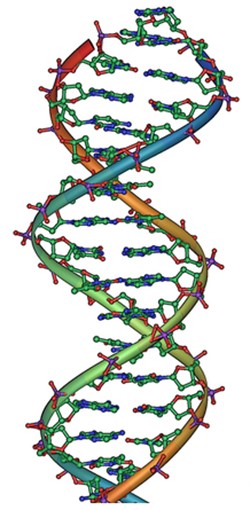
The four nucleotide bases are given the symbols A (adenine), C (cytosine), G (guanine), and T (thymine). The order of the four bases varies in each strand, but the pairing between bases is always the same. C and G are always paired and A and T are always paired, which helps to preserve the order of bases in cell division (mitosis) so as to pass on the correct genetic information. Since the Coulomb force drops with distance ( ), the distances between the base pairs must be small enough that the electrostatic force is sufficient to hold them together.
DNA is a highly charged molecule, with about (fundamental charge) per m. The distance separating the two strands that make up the DNA structure is about 1 nm, while the distance separating the individual atoms within each base is about 0.3 nm.
One might wonder why electrostatic forces do not play a larger role in biology than they do if we have so many charged molecules. The reason is that the electrostatic force is “diluted” due to screening between molecules. This is due to the presence of other charges in the cell.
The best example of this charge screening is the water molecule, represented as . Water is a strongly polar molecule . Its 10 electrons (8 from the oxygen atom and 2 from the two hydrogen atoms) tend to remain closer to the oxygen nucleus than the hydrogen nuclei. This creates two centers of equal and opposite charges—what is called a dipole , as illustrated in [link] . The magnitude of the dipole is called the dipole moment.
These two centers of charge will terminate some of the electric field lines coming from a free charge, as on a DNA molecule. This results in a reduction in the strength of the Coulomb interaction . One might say that screening makes the Coulomb force a short range force rather than long range.
Other ions of importance in biology that can reduce or screen Coulomb interactions are and and . These ions are located both inside and outside of living cells. The movement of these ions through cell membranes is crucial to the motion of nerve impulses through nerve axons.
Recent studies of electrostatics in biology seem to show that electric fields in cells can be extended over larger distances, in spite of screening, by “microtubules” within the cell. These microtubules are hollow tubes composed of proteins that guide the movement of chromosomes when cells divide, the motion of other organisms within the cell, and provide mechanisms for motion of some cells (as motors).
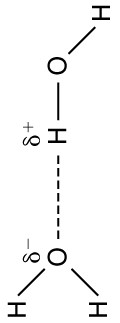
A cell membrane is a thin layer enveloping a cell. The thickness of the membrane is much less than the size of the cell. In a static situation the membrane has a charge distribution of C/m 2 on its inner surface and C/m 2 on its outer surface. Draw a diagram of the cell and the surrounding cell membrane. Include on this diagram the charge distribution and the corresponding electric field. Is there any electric field inside the cell? Is there any electric field outside the cell?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?