| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
What do taking off in a jet airplane, turning a corner in a car, riding a merry-go-round, and the circular motion of a tropical cyclone have in common? Each exhibits fictitious forces—unreal forces that arise from motion and may seem real, because the observer’s frame of reference is accelerating or rotating.
When taking off in a jet, most people would agree it feels as if you are being pushed back into the seat as the airplane accelerates down the runway. Yet a physicist would say that you tend to remain stationary while the seat pushes forward on you, and there is no real force backward on you. An even more common experience occurs when you make a tight curve in your car—say, to the right. You feel as if you are thrown (that is, forced ) toward the left relative to the car. Again, a physicist would say that you are going in a straight line but the car moves to the right, and there is no real force on you to the left. Recall Newton’s first law.
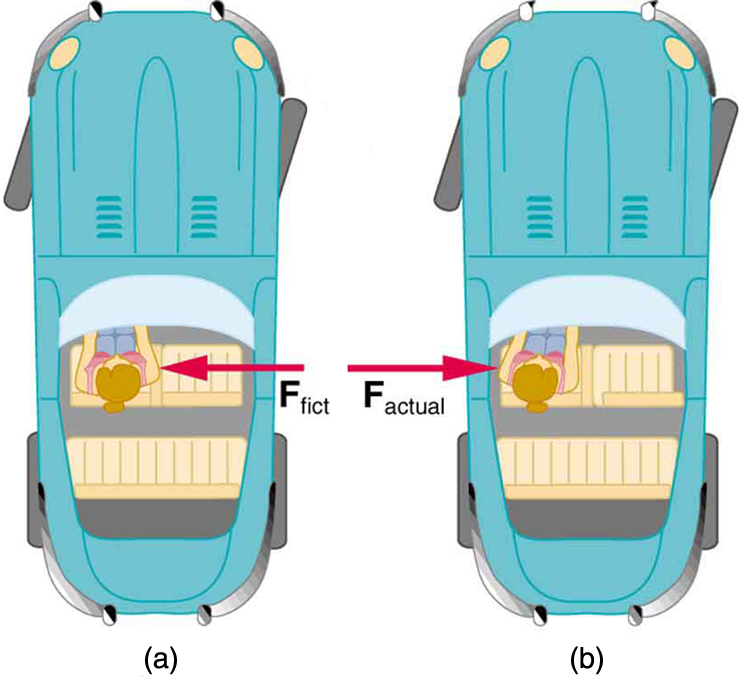
We can reconcile these points of view by examining the frames of reference used. Let us concentrate on people in a car. Passengers instinctively use the car as a frame of reference, while a physicist uses Earth. The physicist chooses Earth because it is very nearly an inertial frame of reference—one in which all forces are real (that is, in which all forces have an identifiable physical origin). In such a frame of reference, Newton’s laws of motion take the form given in Dynamics: Newton's Laws of Motion The car is a non-inertial frame of reference because it is accelerated to the side. The force to the left sensed by car passengers is a fictitious force having no physical origin. There is nothing real pushing them left—the car, as well as the driver, is actually accelerating to the right.
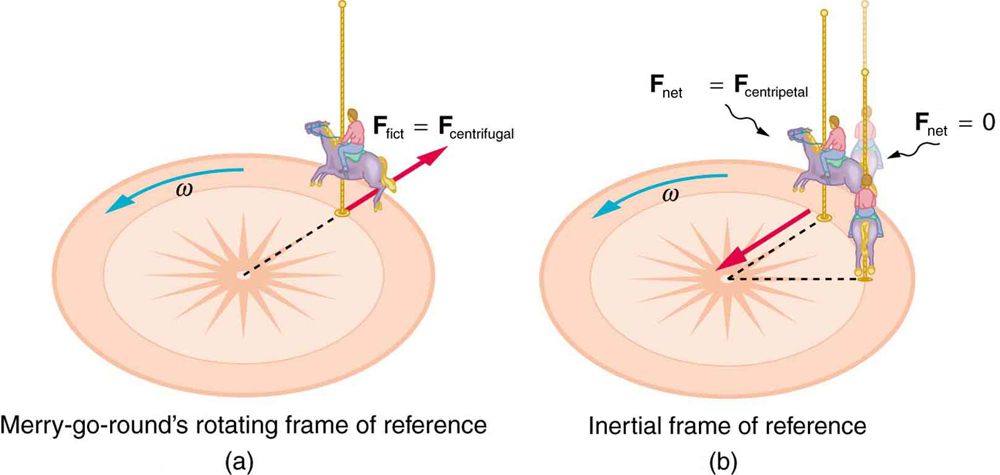
Let us now take a mental ride on a merry-go-round—specifically, a rapidly rotating playground merry-go-round. You take the merry-go-round to be your frame of reference because you rotate together. In that non-inertial frame, you feel a fictitious force, named centrifugal force ( not to be confused with centripetal force ) , trying to throw you off. You must hang on tightly to counteract the centrifugal force. In Earth’s frame of reference, there is no force trying to throw you off. Rather you must hang on to make yourself go in a circle because otherwise you would go in a straight line, right off the merry-go-round.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?