| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Unstable nuclei decay. However, some nuclides decay faster than others. For example, radium and polonium, discovered by the Curies, decay faster than uranium. This means they have shorter lifetimes, producing a greater rate of decay. In this section we explore half-life and activity, the quantitative terms for lifetime and rate of decay.
Why use a term like half-life rather than lifetime? The answer can be found by examining [link] , which shows how the number of radioactive nuclei in a sample decreases with time. The time in which half of the original number of nuclei decay is defined as the half-life , . Half of the remaining nuclei decay in the next half-life. Further, half of that amount decays in the following half-life. Therefore, the number of radioactive nuclei decreases from to in one half-life, then to in the next, and to in the next, and so on. If is a large number, then many half-lives (not just two) pass before all of the nuclei decay. Nuclear decay is an example of a purely statistical process. A more precise definition of half-life is that each nucleus has a 50% chance of living for a time equal to one half-life . Thus, if is reasonably large, half of the original nuclei decay in a time of one half-life. If an individual nucleus makes it through that time, it still has a 50% chance of surviving through another half-life. Even if it happens to make it through hundreds of half-lives, it still has a 50% chance of surviving through one more. The probability of decay is the same no matter when you start counting. This is like random coin flipping. The chance of heads is 50%, no matter what has happened before.
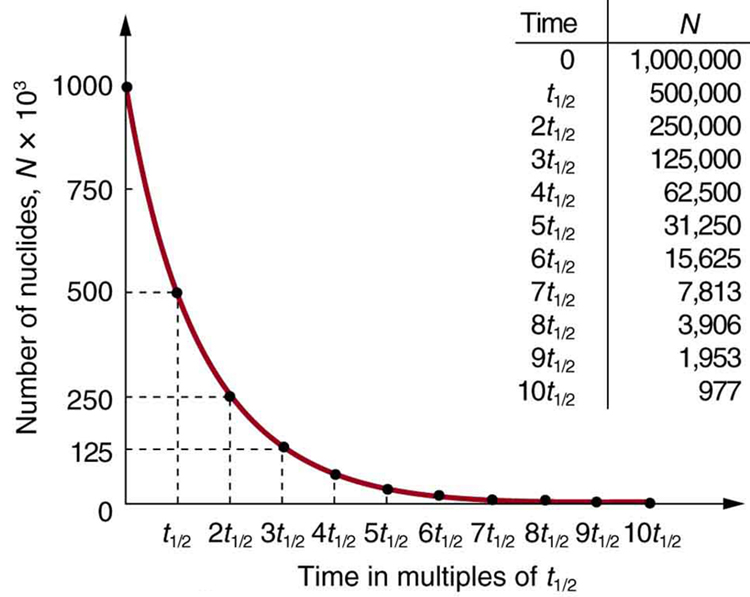
There is a tremendous range in the half-lives of various nuclides, from as short as s for the most unstable, to more than y for the least unstable, or about 46 orders of magnitude. Nuclides with the shortest half-lives are those for which the nuclear forces are least attractive, an indication of the extent to which the nuclear force can depend on the particular combination of neutrons and protons. The concept of half-life is applicable to other subatomic particles, as will be discussed in Particle Physics . It is also applicable to the decay of excited states in atoms and nuclei. The following equation gives the quantitative relationship between the original number of nuclei present at time zero ( ) and the number ( ) at a later time :
where is the base of the natural logarithm, and is the decay constant for the nuclide. The shorter the half-life, the larger is the value of , and the faster the exponential decreases with time. The relationship between the decay constant and the half-life is

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?