| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Nuclear decay has provided an amazing window into the realm of the very small. Nuclear decay gave the first indication of the connection between mass and energy, and it revealed the existence of two of the four basic forces in nature. In this section, we explore the major modes of nuclear decay; and, like those who first explored them, we will discover evidence of previously unknown particles and conservation laws.
Some nuclides are stable, apparently living forever. Unstable nuclides decay (that is, they are radioactive), eventually producing a stable nuclide after many decays. We call the original nuclide the parent and its decay products the daughters . Some radioactive nuclides decay in a single step to a stable nucleus. For example, is unstable and decays directly to , which is stable. Others, such as , decay to another unstable nuclide, resulting in a decay series in which each subsequent nuclide decays until a stable nuclide is finally produced. The decay series that starts from is of particular interest, since it produces the radioactive isotopes and , which the Curies first discovered (see [link] ). Radon gas is also produced ( in the series), an increasingly recognized naturally occurring hazard. Since radon is a noble gas, it emanates from materials, such as soil, containing even trace amounts of and can be inhaled. The decay of radon and its daughters produces internal damage. The decay series ends with , a stable isotope of lead.
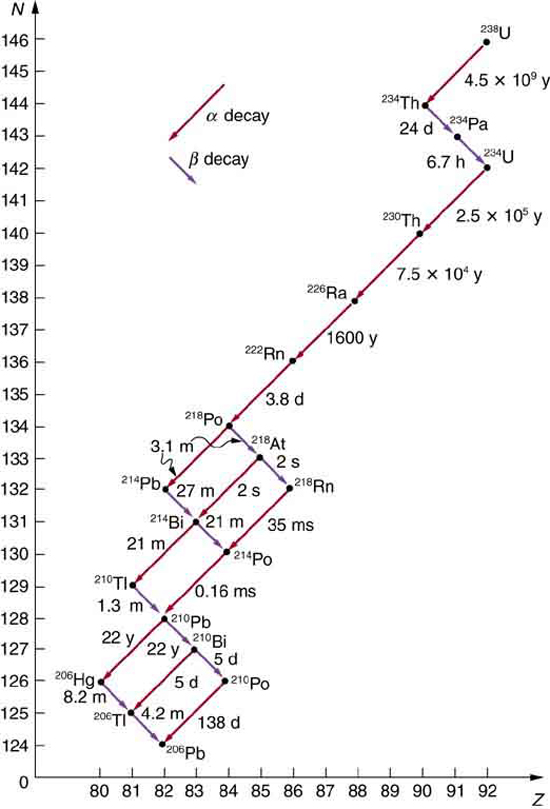
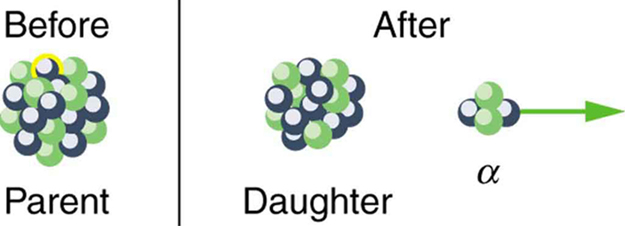
Note that the daughters of decay shown in [link] always have two fewer protons and two fewer neutrons than the parent. This seems reasonable, since we know that decay is the emission of a nucleus, which has two protons and two neutrons. The daughters of decay have one less neutron and one more proton than their parent. Beta decay is a little more subtle, as we shall see. No decays are shown in the figure, because they do not produce a daughter that differs from the parent.
In alpha decay , a nucleus simply breaks away from the parent nucleus, leaving a daughter with two fewer protons and two fewer neutrons than the parent (see [link] ). One example of decay is shown in [link] for . Another nuclide that undergoes decay is . The decay equations for these two nuclides are
and

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?