| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Energy is quantized in some systems, meaning that the system can have only certain energies and not a continuum of energies, unlike the classical case. This would be like having only certain speeds at which a car can travel because its kinetic energy can have only certain values. We also find that some forms of energy transfer take place with discrete lumps of energy. While most of us are familiar with the quantization of matter into lumps called atoms, molecules, and the like, we are less aware that energy, too, can be quantized. Some of the earliest clues about the necessity of quantum mechanics over classical physics came from the quantization of energy.
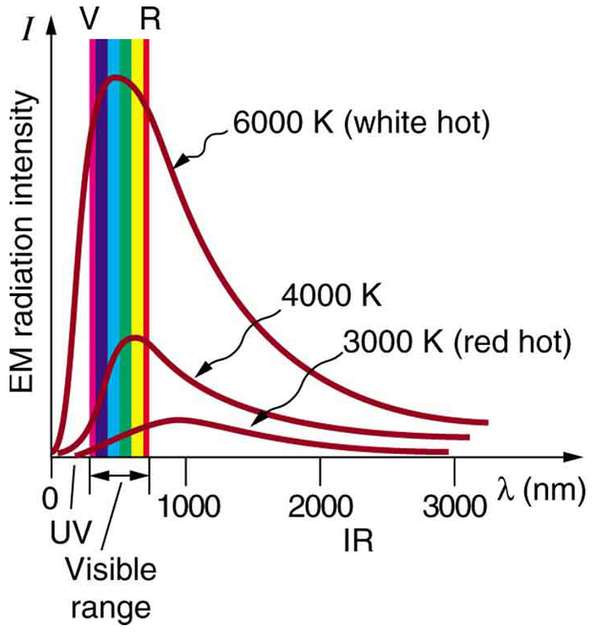
Where is the quantization of energy observed? Let us begin by considering the emission and absorption of electromagnetic (EM) radiation. The EM spectrum radiated by a hot solid is linked directly to the solid’s temperature. (See [link] .) An ideal radiator is one that has an emissivity of 1 at all wavelengths and, thus, is jet black. Ideal radiators are therefore called blackbodies , and their EM radiation is called blackbody radiation . It was discussed that the total intensity of the radiation varies as the fourth power of the absolute temperature of the body, and that the peak of the spectrum shifts to shorter wavelengths at higher temperatures. All of this seems quite continuous, but it was the curve of the spectrum of intensity versus wavelength that gave a clue that the energies of the atoms in the solid are quantized. In fact, providing a theoretical explanation for the experimentally measured shape of the spectrum was a mystery at the turn of the century. When this “ultraviolet catastrophe” was eventually solved, the answers led to new technologies such as computers and the sophisticated imaging techniques described in earlier chapters. Once again, physics as an enabling science changed the way we live.
The German physicist Max Planck (1858–1947) used the idea that atoms and molecules in a body act like oscillators to absorb and emit radiation. The energies of the oscillating atoms and molecules had to be quantized to correctly describe the shape of the blackbody spectrum. Planck deduced that the energy of an oscillator having a frequency is given by
Here is any nonnegative integer (0, 1, 2, 3, …). The symbol stands for Planck’s constant , given by
The equation means that an oscillator having a frequency (emitting and absorbing EM radiation of frequency ) can have its energy increase or decrease only in discrete steps of size

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?