| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Telescopes are meant for viewing distant objects, producing an image that is larger than the image that can be seen with the unaided eye. Telescopes gather far more light than the eye, allowing dim objects to be observed with greater magnification and better resolution. Although Galileo is often credited with inventing the telescope, he actually did not. What he did was more important. He constructed several early telescopes, was the first to study the heavens with them, and made monumental discoveries using them. Among these are the moons of Jupiter, the craters and mountains on the Moon, the details of sunspots, and the fact that the Milky Way is composed of vast numbers of individual stars.
[link] (a) shows a telescope made of two lenses, the convex objective and the concave eyepiece, the same construction used by Galileo. Such an arrangement produces an upright image and is used in spyglasses and opera glasses.
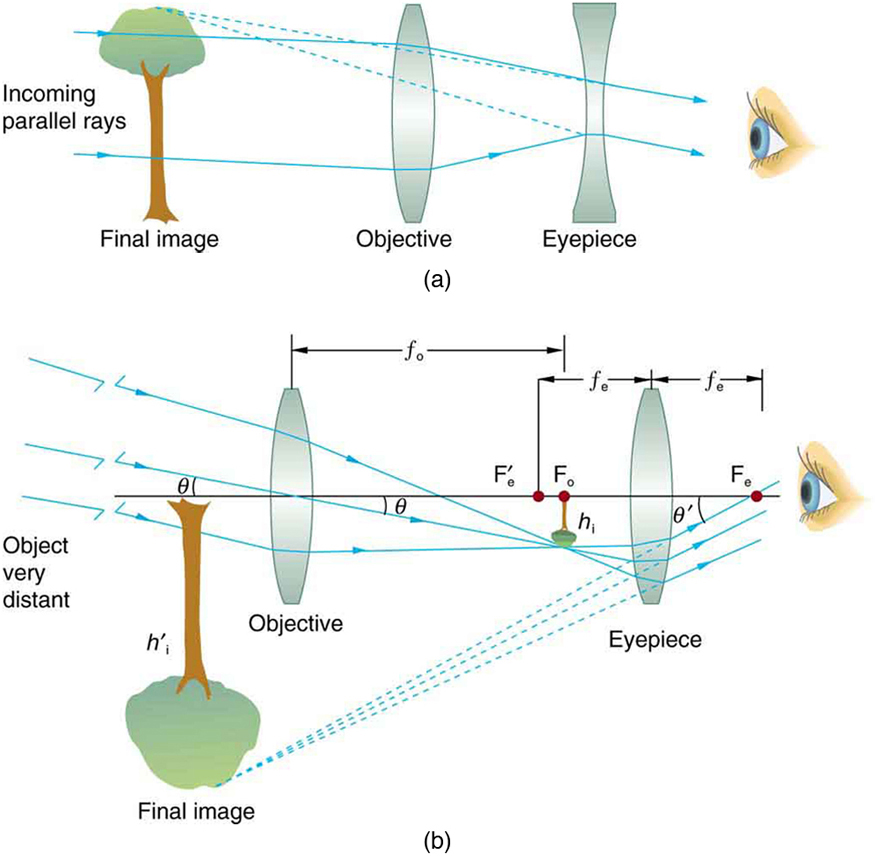
The most common two-lens telescope, like the simple microscope, uses two convex lenses and is shown in [link] (b). The object is so far away from the telescope that it is essentially at infinity compared with the focal lengths of the lenses ( ). The first image is thus produced at , as shown in the figure. To prove this, note that
Because , this simplifies to
which implies that , as claimed. It is true that for any distant object and any lens or mirror, the image is at the focal length.
The first image formed by a telescope objective as seen in [link] (b) will not be large compared with what you might see by looking at the object directly. For example, the spot formed by sunlight focused on a piece of paper by a magnifying glass is the image of the Sun, and it is small. The telescope eyepiece (like the microscope eyepiece) magnifies this first image. The distance between the eyepiece and the objective lens is made slightly less than the sum of their focal lengths so that the first image is closer to the eyepiece than its focal length. That is, is less than , and so the eyepiece forms a case 2 image that is large and to the left for easy viewing. If the angle subtended by an object as viewed by the unaided eye is , and the angle subtended by the telescope image is , then the angular magnification is defined to be their ratio. That is, . It can be shown that the angular magnification of a telescope is related to the focal lengths of the objective and eyepiece; and is given by
The minus sign indicates the image is inverted. To obtain the greatest angular magnification, it is best to have a long focal length objective and a short focal length eyepiece. The greater the angular magnification , the larger an object will appear when viewed through a telescope, making more details visible. Limits to observable details are imposed by many factors, including lens quality and atmospheric disturbance.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?