| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
A good-quality mirror may reflect more than 90% of the light that falls on it, absorbing the rest. But it would be useful to have a mirror that reflects all of the light that falls on it. Interestingly, we can produce total reflection using an aspect of refraction .
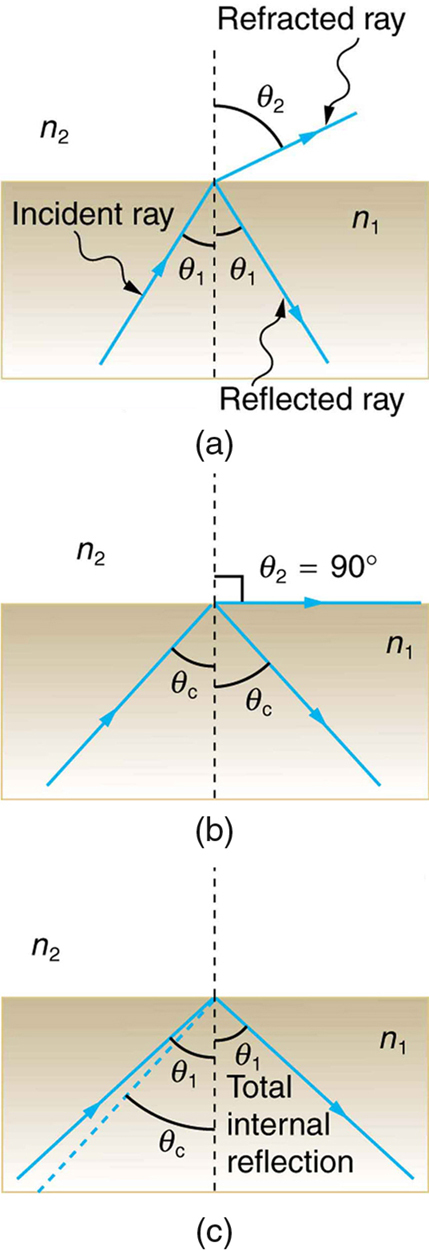
Consider what happens when a ray of light strikes the surface between two materials, such as is shown in [link] (a). Part of the light crosses the boundary and is refracted; the rest is reflected. If, as shown in the figure, the index of refraction for the second medium is less than for the first, the ray bends away from the perpendicular. (Since , the angle of refraction is greater than the angle of incidence—that is, .) Now imagine what happens as the incident angle is increased. This causes to increase also. The largest the angle of refraction can be is , as shown in [link] (b).The critical angle for a combination of materials is defined to be the incident angle that produces an angle of refraction of . That is, is the incident angle for which . If the incident angle is greater than the critical angle, as shown in [link] (c), then all of the light is reflected back into medium 1, a condition called total internal reflection .
Snell’s law states the relationship between angles and indices of refraction. It is given by
When the incident angle equals the critical angle ( ), the angle of refraction is ( ). Noting that , Snell’s law in this case becomes
The critical angle for a given combination of materials is thus
Total internal reflection occurs for any incident angle greater than the critical angle , and it can only occur when the second medium has an index of refraction less than the first. Note the above equation is written for a light ray that travels in medium 1 and reflects from medium 2, as shown in the figure.
What is the critical angle for light traveling in a polystyrene (a type of plastic) pipe surrounded by air?
Strategy
The index of refraction for polystyrene is found to be 1.49 in [link] , and the index of refraction of air can be taken to be 1.00, as before. Thus, the condition that the second medium (air) has an index of refraction less than the first (plastic) is satisfied, and the equation can be used to find the critical angle . Here, then, and .
Solution
The critical angle is given by
Substituting the identified values gives
Discussion
This means that any ray of light inside the plastic that strikes the surface at an angle greater than will be totally reflected. This will make the inside surface of the clear plastic a perfect mirror for such rays without any need for the silvering used on common mirrors. Different combinations of materials have different critical angles, but any combination with can produce total internal reflection. The same calculation as made here shows that the critical angle for a ray going from water to air is , while that from diamond to air is , and that from flint glass to crown glass is . There is no total reflection for rays going in the other direction—for example, from air to water—since the condition that the second medium must have a smaller index of refraction is not satisfied. A number of interesting applications of total internal reflection follow.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?