| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
We know that the current through an inductor cannot be turned on or off instantaneously. The change in current changes flux, inducing an emf opposing the change (Lenz’s law). How long does the opposition last? Current will flow and can be turned off, but how long does it take? [link] shows a switching circuit that can be used to examine current through an inductor as a function of time.
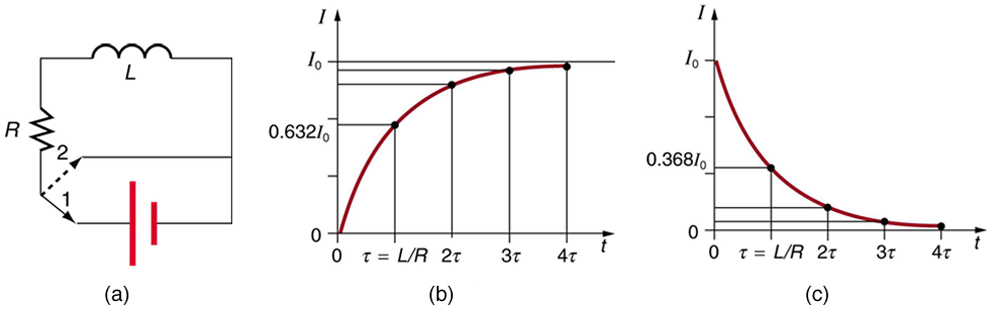
When the switch is first moved to position 1 (at ), the current is zero and it eventually rises to , where is the total resistance of the circuit. The opposition of the inductor is greatest at the beginning, because the amount of change is greatest. The opposition it poses is in the form of an induced emf, which decreases to zero as the current approaches its final value. The opposing emf is proportional to the amount of change left. This is the hallmark of an exponential behavior, and it can be shown with calculus that
is the current in an RL circuit when switched on (Note the similarity to the exponential behavior of the voltage on a charging capacitor). The initial current is zero and approaches with a characteristic time constant for an RL circuit, given by
where has units of seconds, since . In the first period of time , the current rises from zero to , since . The current will go 0.632 of the remainder in the next time . A well-known property of the exponential is that the final value is never exactly reached, but 0.632 of the remainder to that value is achieved in every characteristic time . In just a few multiples of the time , the final value is very nearly achieved, as the graph in [link] (b) illustrates.
The characteristic time depends on only two factors, the inductance and the resistance . The greater the inductance , the greater is, which makes sense since a large inductance is very effective in opposing change. The smaller the resistance , the greater is. Again this makes sense, since a small resistance means a large final current and a greater change to get there. In both cases—large and small —more energy is stored in the inductor and more time is required to get it in and out.
When the switch in [link] (a) is moved to position 2 and cuts the battery out of the circuit, the current drops because of energy dissipation by the resistor. But this is also not instantaneous, since the inductor opposes the decrease in current by inducing an emf in the same direction as the battery that drove the current. Furthermore, there is a certain amount of energy, , stored in the inductor, and it is dissipated at a finite rate. As the current approaches zero, the rate of decrease slows, since the energy dissipation rate is . Once again the behavior is exponential, and is found to be

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?