| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |

Most waves do not look very simple. They look more like the waves in [link] than like the simple water wave considered in Waves . (Simple waves may be created by a simple harmonic oscillation, and thus have a sinusoidal shape). Complex waves are more interesting, even beautiful, but they look formidable. Most waves appear complex because they result from several simple waves adding together. Luckily, the rules for adding waves are quite simple.
When two or more waves arrive at the same point, they superimpose themselves on one another. More specifically, the disturbances of waves are superimposed when they come together—a phenomenon called superposition . Each disturbance corresponds to a force, and forces add. If the disturbances are along the same line, then the resulting wave is a simple addition of the disturbances of the individual waves—that is, their amplitudes add. [link] and [link] illustrate superposition in two special cases, both of which produce simple results.
[link] shows two identical waves that arrive at the same point exactly in phase. The crests of the two waves are precisely aligned, as are the troughs. This superposition produces pure constructive interference . Because the disturbances add, pure constructive interference produces a wave that has twice the amplitude of the individual waves, but has the same wavelength.
[link] shows two identical waves that arrive exactly out of phase—that is, precisely aligned crest to trough—producing pure destructive interference . Because the disturbances are in the opposite direction for this superposition, the resulting amplitude is zero for pure destructive interference—the waves completely cancel.
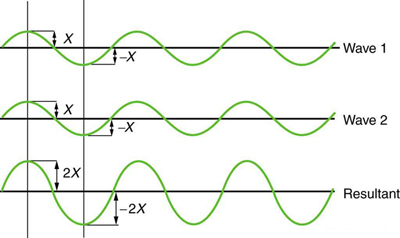
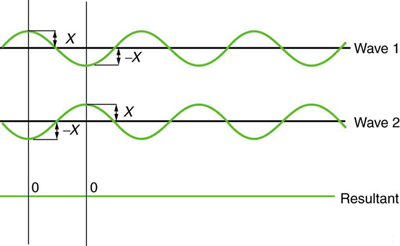
While pure constructive and pure destructive interference do occur, they require precisely aligned identical waves. The superposition of most waves produces a combination of constructive and destructive interference and can vary from place to place and time to time. Sound from a stereo, for example, can be loud in one spot and quiet in another. Varying loudness means the sound waves add partially constructively and partially destructively at different locations. A stereo has at least two speakers creating sound waves, and waves can reflect from walls. All these waves superimpose. An example of sounds that vary over time from constructive to destructive is found in the combined whine of airplane jets heard by a stationary passenger. The combined sound can fluctuate up and down in volume as the sound from the two engines varies in time from constructive to destructive. These examples are of waves that are similar.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?