| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
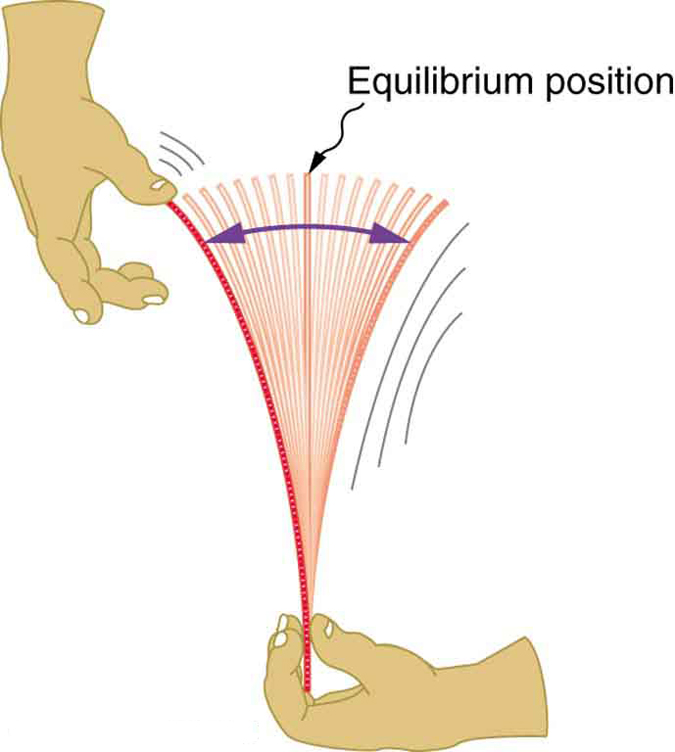
Newton’s first law implies that an object oscillating back and forth is experiencing forces. Without force, the object would move in a straight line at a constant speed rather than oscillate. Consider, for example, plucking a plastic ruler to the left as shown in [link] . The deformation of the ruler creates a force in the opposite direction, known as a restoring force . Once released, the restoring force causes the ruler to move back toward its stable equilibrium position, where the net force on it is zero. However, by the time the ruler gets there, it gains momentum and continues to move to the right, producing the opposite deformation. It is then forced to the left, back through equilibrium, and the process is repeated until dissipative forces dampen the motion. These forces remove mechanical energy from the system, gradually reducing the motion until the ruler comes to rest.
The simplest oscillations occur when the restoring force is directly proportional to displacement. When stress and strain were covered in Newton’s Third Law of Motion , the name was given to this relationship between force and displacement was Hooke’s law:
Here, is the restoring force, is the displacement from equilibrium or deformation , and is a constant related to the difficulty in deforming the system. The minus sign indicates the restoring force is in the direction opposite to the displacement.
The force constant is related to the rigidity (or stiffness) of a system—the larger the force constant, the greater the restoring force, and the stiffer the system. The units of are newtons per meter (N/m). For example, is directly related to Young’s modulus when we stretch a string. [link] shows a graph of the absolute value of the restoring force versus the displacement for a system that can be described by Hooke’s law—a simple spring in this case. The slope of the graph equals the force constant in newtons per meter. A common physics laboratory exercise is to measure restoring forces created by springs, determine if they follow Hooke’s law, and calculate their force constants if they do.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?