| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |

The expression “it’s not the heat, it’s the humidity” makes a valid point. We keep cool in hot weather by evaporating sweat from our skin and water from our breathing passages. Because evaporation is inhibited by high humidity, we feel hotter at a given temperature when the humidity is high. Low humidity, on the other hand, can cause discomfort from excessive drying of mucous membranes and can lead to an increased risk of respiratory infections.
When we say humidity, we really mean relative humidity . Relative humidity tells us how much water vapor is in the air compared with the maximum possible. At its maximum, denoted as saturation , the relative humidity is 100%, and evaporation is inhibited. The amount of water vapor in the air depends on temperature. For example, relative humidity rises in the evening, as air temperature declines, sometimes reaching the dew point . At the dew point temperature, relative humidity is 100%, and fog may result from the condensation of water droplets if they are small enough to stay in suspension. Conversely, if you wish to dry something (perhaps your hair), it is more effective to blow hot air over it rather than cold air, because, among other things, the increase in temperature increases the energy of the molecules, so the rate of evaporation increases.
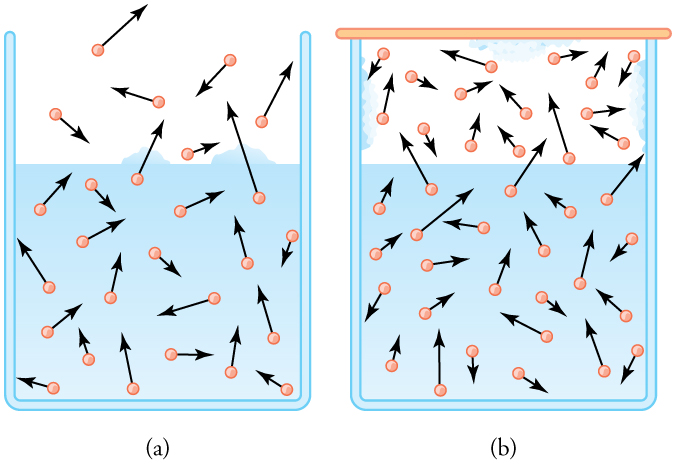
The amount of water vapor in the air depends on the vapor pressure of water. The liquid and solid phases are continuously giving off vapor because some of the molecules have high enough speeds to enter the gas phase; see [link] (a). If a lid is placed over the container, as in [link] (b), evaporation continues, increasing the pressure, until sufficient vapor has built up for condensation to balance evaporation. Then equilibrium has been achieved, and the vapor pressure is equal to the partial pressure of water in the container. Vapor pressure increases with temperature because molecular speeds are higher as temperature increases. [link] gives representative values of water vapor pressure over a range of temperatures.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?