| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Background
Electricity is a type of energy. An object has electrical energy when it has the ability to conduct electricity. Electricity is measured in Volts.
Electrical energy can be easily converted to other forms of electricity.
There are two main types of electricity:
Battery-electricity
Electrical energy are stored in batteries. The energy in batteries are called chemical energy. When electrical energy moves, the electrons flows in an electrical circuit.
The basic elements of an electrical circuit is:
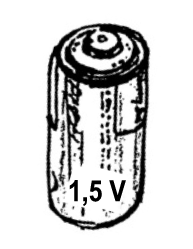
a source of energy e.g. a battery
| Sketch | Symbol |
 |
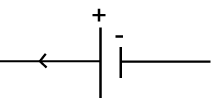 |
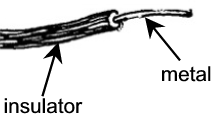
a conductor e.g. a sort of metal in the shape of a wire
| Sketch | Symbol |
 |
 |
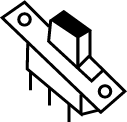
a switch to form an open or closed circuit
| Sketch | Symbol |
 |
|
a load e.g. a source of light, sound, motion or heat
| Sketch | Symbol |
a light
 |
 |
a buzzer
 |
 |
an electrical motor
 |
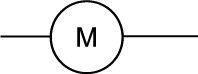 |
Two or more of the same component in an electric circuit can be connected in two different ways in the circuit;
Advantage of cells in series – current supply becomes more powerful
Advantage of cells in parallel – the cells can produce the same current for longer.
To the teacher:
These worksheets should be done in groups. Each group can construct a different circuit and then explain it to the rest of the class before completing a worksheet. A class should be divided into 7 groups, because there are 7 worksheets. This would save a huge amount of time. Each group should construct a test circuit with a switch, 1,5 V lamp, lamp holder and a 1,5 V cell in a cell holder. First screw the holders and switch on the board, add the wire between them and then add the cell and lightbulb.
Equipment and tools needed:
WORKSHEET 1:
1.3 Draw a circuit diagram of the circuit, using the correct symbols.
1.4 Underline:
The light bulb shines (very brightly/bright/dimly/ not at all).
WORKSHEET 2:
2.1 Connect one 1,5 V cell in a cell holder to two 1,5 V lamps in two lamp holders in parallel using wire and adding a switch on a piece of insulation board.
The light bulbs shine (very brightly/ brightly/ dimly/ not at all).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Technology grade 7' conversation and receive update notifications?