| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In this module some of the basic classifications of systems will be briefly introduced and the most important propertiesof these systems are explained. As can be seen, the properties of a system provide an easy way to distinguish onesystem from another. Understanding these basic differences between systems, and their properties, will be a fundamentalconcept used in all signal and system courses. Once a set of systems can be identified as sharing particular properties, one no longer hasto reprove a certain characteristic of a system each time, but it can simply be known due to the the systemclassification.
One of the most important distinctions to understand is the difference between discrete time and continuous time systems. A system in which the input signal and output signal both have continuous domains is said to be a continuous system. One in which the input signal and output signal both have discrete domains is said to be a discrete system. Of course, it is possible to conceive of signals that belong to neither category, such as systems in which sampling of a continuous time signal or reconstruction from a discrete time signal take place.
A linear system is any system that obeys the properties of scaling (first order homogeneity) and superposition (additivity) further described below. A nonlinear system is any system that does not have at least one of these properties.
To show that a system obeys the scaling property is to show that
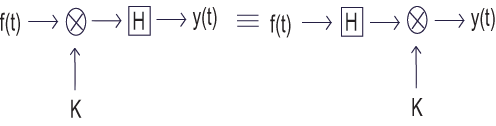
To demonstrate that a system obeys thesuperposition property of linearity is to show that
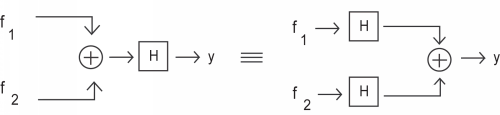
It is possible to check a system for linearity in a single (though larger) step. To do this, simply combine the firsttwo steps to get
A system is said to be time invariant if it commutes with the parameter shift operator defined by for all , which is to say
for all real . Intuitively, that means that for any input function that produces some output function, any time shift of that input function will produce an output function identical in every way except that it is shifted by the same amount. Any system that does not have this property is said to be time varying.
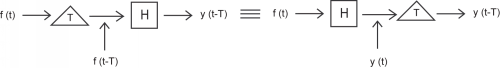
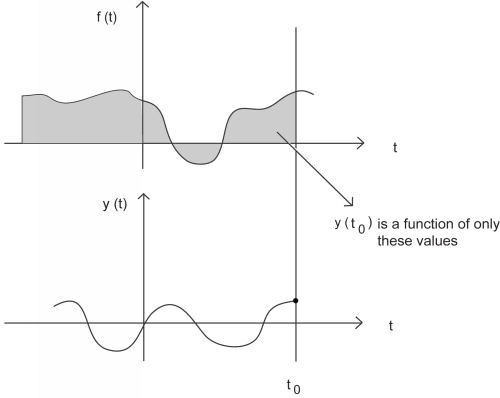
A causal system is one in which the output depends only on current or past inputs, but not future inputs. Similarly, an anticausal system is one in which the output depends only on current or future inputs, but not past inputs. Finally, a noncausal system is one in which the output depends on both past and future inputs. All "realtime" systems must be causal, since they can not have future inputs available to them.
One may think the idea of future inputs does not seem to make much physical sense; however, we have only beendealing with time as our dependent variable so far, which is not always the case. Imagine rather that we wanted to doimage processing. Then the dependent variable might represent pixel positions to the left and right (the "future") of the currentposition on the image, and we would not necessarily have a causal system.

There are several definitions of stability, but the one that will be used most frequently in this course will be bounded input, bounded output (BIBO) stability. In this context, a stable system is one in which the output is bounded if the input is also bounded. Similarly, an unstable system is one in which at least one bounded input produces an unbounded output.
Representing this mathematically, a stable system must have the following property, where is the input and is the output. The output must satisfy the condition
This module describes just some of the many ways in which systems can be classified. Systems can be continuous time, discrete time, or neither. They can be linear or nonlinear, time invariant or time varying, and stable or unstable. We can also divide them based on their causality properties. There are other ways to classify systems, such as use of memory, that are not discussed here but will be described in subsequent modules.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Signals and systems' conversation and receive update notifications?