| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Another interesting fact she found is that the factory controls very carefully that the packets do not contain too few raisins. They aim to have at least 75 in the 50g packet, 150 in the 100g packet and 300 in the 200g packet. To be sure that this happens, they are careful to make the packet of raisins with the same final mass. They also put a few extra raisins in most packets. Olga was very happy to tell them that her figures agreed with their standards.
From the given information, find out how much the raisins (excluding the packaging) cost. Give your answer in rand per kilogram.
| LO 2 |
| Patterns, Functions and AlgebraThe learner will be able to recognise, describe and represent patterns and relationships, as well as to solve problems using algebraic language and skills. |
| We know this when the learner: |
| 2.1 investigates, in different ways, a variety of numeric and geometric patterns and relationships by representing and generalising them, and by explaining and justifying the rules that generate them (including patterns found in nature and cultural forms and patterns of the learner’s own creation; |
| 2.2 represents and uses relationships between variables in order to determine input and/or output values in a variety of ways using: |
| 2.2.1 verbal descriptions; |
| 2.2.2 flow diagrams; |
| 2.2.3 tables; |
| 2.2.4 formulae and equations; |
| 2.3 constructs mathematical models that represent, describe and provide solutions to problem situations, showing responsibility toward the environment and health of others (including problems within human rights, social, economic, cultural and environmental contexts); |
| 2.4 solves equations by inspection, trial-and-improvement or algebraic processes (additive and multiplicative inverses, and factorisation), checking the solution by substitution; |
| 2.5 draws graphs on the Cartesian plane for given equations (in two variables), or determines equations or formulae from given graphs using tables where necessary; |
| 2.6 determines, analyses and interprets the equivalence of different descriptions of the same relationship or rule presented: |
| 2.6.1 verbally; |
| 2.6.2 in flow diagrams; |
| 2.6.3 in tables; |
| 2.6.4 by equations or expressions; |
| 2.6.5 by graphs on the Cartesian plane in order to select the most useful representation for a given situation; |
| 2.8 uses the laws of exponents to simplify expressions and solve equations; |
| 2.9 uses factorisation to simplify algebraic expressions and solve equations. |
Discussion
Answers:
1 480 black; 960 white; 300 red; 240 yellow; 240 blue and 180 green
2 480 black; 960 white; 675 red; 540 yellow; 540 blue and 405 green
5.
| Side length of triangle in centimetres | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| Number of beads per triangle | 3 | 6 | 10 | 15 | 21 | 28 | 36 |
| Perimeter of triangle | 6 | 9 | 12 | 15 | 18 | 21 | 24 |
6.
| Size of necklace | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | x |
| Number of triangular motifs | 1 | 3 | 6 | 10 | 15 | x +( x –1)+( x –2)+ … +1 |
| Number of triangular spaces | 0 | 1 | 3 | 6 | 10 | ( x –1)+( x –2)+ … +1 |
| Number of beads on each side of triangular motif | 4 | 8 | 12 | 16 | 20 | 4 x |
| Total number of beads in necklace | 10 | 30 | 60 | 100 | 150 | 10{ x +( x –1)+( x –2)+ … +1} |
| Number of black beads | 1 | 3 | 6 | 10 | 15 | ( x –1)+( x –2)+ … +1 |
| Total perimeter of pendant with 1cm-diameter beads | 9 | 21 | 33 | 45 | 57 | 3(4 x –1) |
7.
| Size of necklace | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | x |
| Number of triangular motifs | 1 | 3 | 6 | 10 | 15 | x +( x –1)+( x –2)+ … +1 |
| Number of triangular spaces | 0 | 1 | 3 | 6 | 10 | ( x –1)+( x –2)+ … +1 |
| Number of beads on each side of triangular motif | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 5 x |
| Total number of beads in necklace | 15 | 45 | 90 | 150 | 225 | 15{ x +( x –1)+( x –2)+ … +1} |
| Number of black beads | 3 | 9 | 18 | 30 | 45 | 3{ x +( x –1)+( x –2)+ … +1} |
| Total perimeter of pendant with 1cm-diameter beads | 12 | 27 | 42 | 57 | 72 | 3(5 x –1) |
ACTIVITY 2
1.
| Number of days: | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 |
| Away-van: | R750 | 1500 | 2250 | 3000 | 3750 | 4500 | 5250 | 6000 | 6750 | 7500 | 8250 |
| Best Caravans: | R1560 | R1920 | 2280 | 2640 | 3000 | 3360 | 3720 | 4080 | 4440 | 4800 | 5160 |
| Car-a-holiday: | R1490 | R2030 | 2570 | 3110 | 3650 | 4190 | 4730 | 5270 | 5810 | 6350 | 6890 |
If they want to go for only three days then Away-van is the cheapest. Best Caravans is the cheapest for holidays of from 4 to 11 days. Car-a-holiday is never the cheapest option, even if the holiday is longer than11 days.
3. Input = 9; output = 540 × 5 + 950 = 3 650
4.
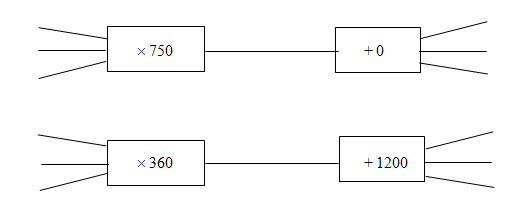
5. Bradley and his phones:
Tables:
| Number of calls: | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| Advanced mobile: | $26 | $32 | $38 | $44 | $50 | $56 |
| Genie rentals: | $24 | $38 | $52 | $66 | $80 | $94 |
| Hi-Pro: | $40 | $50 | $60 | $70 | $80 | $90 |

6. Genie Rentals is the cheapest as long as he won’t want to make more than about 10 calls. Hi-Pro is never the cheapest. He is likely to get the best deal from Advanced Mobile if he wants to stay for a while.
7. It is easier to compare costs from the table. A graph would be easier still.
ACTIVITY 3
TEST

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Mathematics grade 9' conversation and receive update notifications?