| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
| The Main Religions According To ContinentsFigures are given in percentages (S.A. = South America. N.A. = North America | |||||||
| Religion | A frica | A sia | E urope | S . A . | N . A . | O ceania | E urasia |
| Christianity | 17,9 | 15,6 | 22,55 | 23,75 | 13,0 | 1,2 | 6,0 |
| Islam | 28,66 | 65,56 | 1,3 | 0,14 | 0,29 | 0,01 | 4,04 |
| Hinduism | 0,2 | 99,37 | 0,1 | 0,1 | 0,17 | 0,059 | 0,001 |
| Buddhism | 0,01 | 99,42 | 0,08 | 0,17 | 0,18 | 0,01 | 0,13 |
| Judaism | 1,89 | 31,35 | 8,24 | 6,13 | 39,29 | 0,55 | 12,55 |
| Six Main Religions | |
| Religion | Number of Adherents |
| Christianity | 1 833 million |
| Islam | 971 million |
| Hinduism | 733 million |
| Buddhism | 315 million |
| Judaism | 13-14,3 million |
Source 3

Judaism 0,3%
Buddhism 5,7%

Hinduism 13,4%
Other 29,6%
Christianity 33,4%
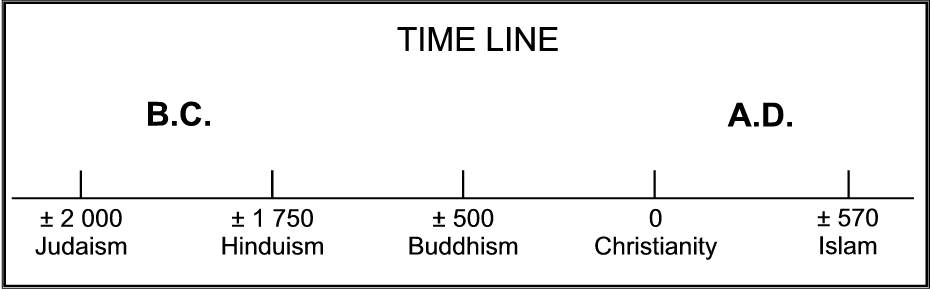
History of Religions
| Judaism | Islam | Hinduism | Buddhism | Christianity |
| 2000 B.C. Abraham, the prophet of Judaism, Christianity and Islam, was born in Ur, the present-day Iraq. | 2000 B.C. According to the Qur'an, Abraham and his son Ishmael built the Kaaba sanctuary in Mecca in present-day Saudi-Arabia. | 1750 B.C. Origin of Hinduism under the influence of Aryan immigrants who worshipped many gods. | 563 - 483 B.C. Siddhartha Gautama, later known as Buddha, founder of Buddhism, lived in Northeast India. | 4 B.C. Jesus Christ, the saviour of the Christian religion was born in Bethlehem, in present-day Israel. |
| Judaism | Islam | Hinduism | Buddhism | Christianity |
| 1200 B.C. The Hebrews settled in Canaan, which roughly corresponded to the present-day Israel. | 570 - 632 A.D. Mohammed, the last and most important Islamic prophet, was born in Mecca. | 1700 B.C. Hindu beliefs revealed to the holy men and orally transmitted. | 100 B.C. The Tripitaka (three baskets), the holy scriptures of Theravada Buddhism, was written. | 30 A.D. Jesus crucified. According to the New Testament, he was resur-rected after three days and ascended to heaven after 40 days. |
| 931 B.C. The kingdom of the Hebrews was split into Israel and Judah. By 900 B.C. the Torah , the first five books of the Bible, had been written. | 610-632 A.D. The angel Gabriel revealed the Qur’an, the Islamic holy scriptures, to Mohammed. It contains 114 chapters. | 1400 B.C. The Rig-Veda, the earliest and most important book of the Vedas, which contain the Hindu precepts, was written. | 20 – 200 A.D. The Sutras (a collection of sayings), the earliest holy books of Mahayana Buddhism, were written. | 40-100 A.D. The New Testament of the Christian Bible as written. Christianity spread through the entire Roman Empire. |
| 587 B.C. The Baby-lonians over-powered Jerusalem, in present-day Israel, and the Israelites were taken into exile. They started to return in varying groups after 539 B.C. | 622 A.D. Mohammed went to Medina in present-day Saudi-Arabia. It was to be the introductory year of the Islamic calendar. | 800 A.D. The Upanishads , the concluding books of the Vedas , were written. They established the idea of Brahman, soul of the universe. | 1506 A.D. St. Peter's basilica, the largest Christian church of all times built in Rome. | |
| 70 A.D. The Romans destroyed Herod's Temple in Jerusalem. The western wall is all that remains of it now. The Jews were scattered through all the countries of the world. |
LEARNING OUTCOME 1: HISTORICAL ENQUIRY The learner will be able to use enquiry skills to investigate the past and present.
We know this when the learner:
1.3 communicates information from sources (reporting):

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'History grade 4' conversation and receive update notifications?