| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The Laplace transform is a generalization of the Continuous-Time Fourier Transform . It is used because the CTFT does not converge/exist for many important signals, and yet it does for the Laplace-transform (e.g., signals with infinite norm). It is also used because it is notationally cleaner than the CTFT. However, instead of using complex exponentials of the form , with purely imaginary parameters, the Laplace transform uses the more general, , where is complex, to analyze signals in terms of exponentially weighted sinusoids.
Although Laplace transforms are rarely solved in practice using integration
(
tables and
computers (
Taking a look at the equations describing the Z-Transform and the Discrete-Time Fourier Transform:
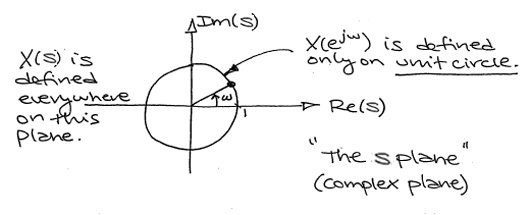
With the Fourier transform, we had a complex-valued function of a purely imaginary variable , . This was something we could envision with two 2-dimensional plots (real and imaginary parts or magnitude andphase). However, with Laplace, we have a complex-valued function of a complex variable . In order to examine the magnitude and phase or real andimaginary parts of this function, we must examine 3-dimensional surface plots of each component.
While these are legitimate ways of looking at a signal in the Laplace domain, it is quite difficult to draw and/or analyze.For this reason, a simpler method has been developed. Although it will not be discussed in detail here, the methodof Poles and Zeros is much easier to understand and is the way both the Laplace transform and its discrete-time counterpart the Z-transform are represented graphically.
Using a computer to find Laplace transforms is relatively
painless. Matlab has two functions,
laplace and
ilaplace , that are both part of the
symbolic toolbox, and will find the Laplace and inverseLaplace transforms respectively. This method is generally
preferred for more complicated functions. Simpler and morecontrived functions are usually found easily enough by
using tables .
Khan lecture on laplace
The laplace transform proves a useful, more general form of the Continuous Time Fourier Transform. It applies equally well to describing systems as well as signals using the eigenfunction method, and to describing a larger class of signals better described using the pole-zero method.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Signals and systems' conversation and receive update notifications?