| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
THE EARLIEST INHABITANTS OF SOUTH AFRICA ALSO WERE THE EARLIEST PEOPLE OF AFRICA. IN THE FOLLOWING MODULES WE WILL STUDY THEIR DWELLINGS, FOOD AND MUSIC.
There are many different groups of people in South Africa and they live in different kinds of homes. Their dwellings have also changed considerably from the simple cave dwellings of the Stone Age to the homes of today. Technological progress has brought about incredible change.
We are going to study indigenous homes, early Cape homesteads, pioneer homes, homesteads in the British architectural style, and certain contemporary houses.
a) This is an exercise in which you simply need to supply missing words! (You will also be doing a quick revision of the earliest homes of the San and the Khoina people.)
The San were nomadic (a) _________ and gatherers. They lived
in caves or shelters made of branches and (b) ________ to protect
them from (c) ______, sun and rain and (d) ____
sleeping in at night. (e) ________ Khoina moved around with their (f)_______
and they therefore lived in (g) ______ huts made of grass mats. The mats
(h) ________ light and could be rolled up (i) ______ they had to
move further (j) ____ young branches were used (k) ________
the frames and they were covered with (l) _________ or grass mats. When
(m) _______ rained, the (n) __________ became swollen with
absorbed water and this prevented the raindrops from getting (o) _____ the
shelter. Many examples of (p) ____ type of dwelling can still be seen (q) ____ Namaqualand.
b) Work in groups when you consult sources to find answers to the following questions:
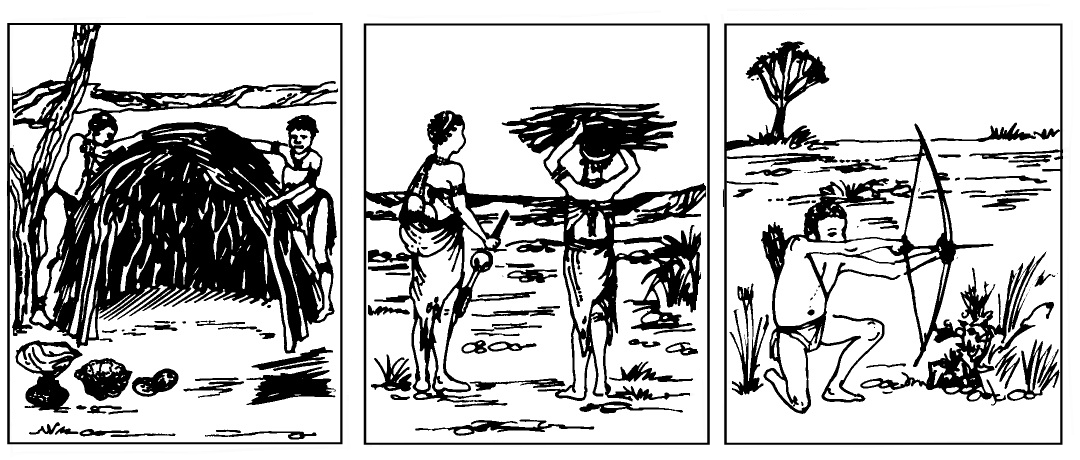
How did the tasks performed by men differ from those performed by women?
What are the differences and similarities that you notice?
Who are these people?
Where did they live?
When did they live?
How did they live?
The San loved listening to stories that explained natural occurrences when they gathered together around the campfire. Make up your own stories about why there are spots on the moon.
c) Look closely at the following sketch of the dwellings of the Khoina, and report back as a group:
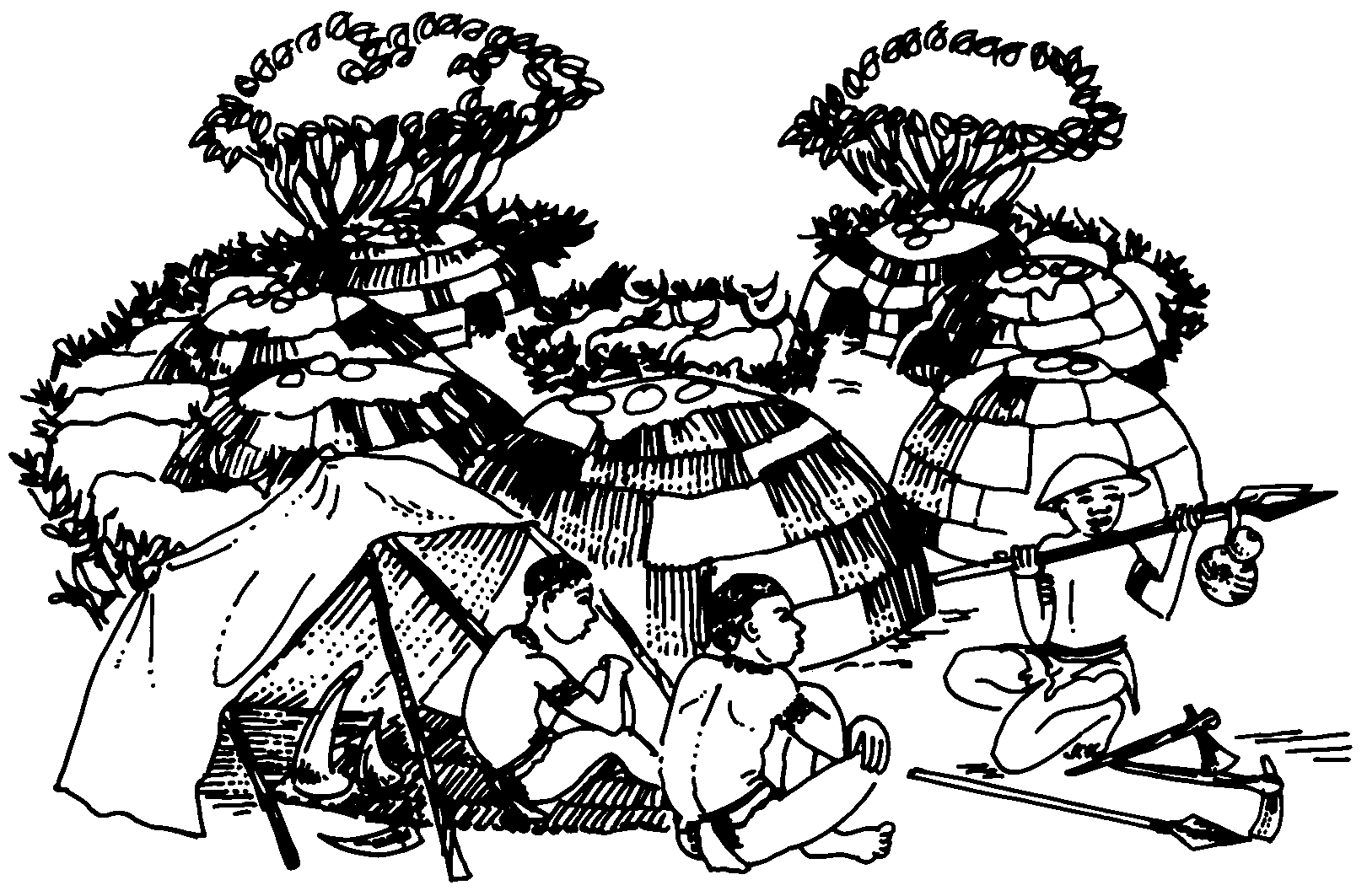
How did they make their huts? What was used for the floors? What is used for the floors in your house?
Why were the huts arranged around the hut belonging to the chief?
On what did they sleep at night? On what do you sleep?
Where did they get water? How are your schools and houses supplied with water?
Why did the Khoina have more possessions than the San?
Supppose a man among the Khoina became blind. How would he have to adapt his lifestyle? (In the short term and in the long term)
d) The Nguni peoples mainly built round huts of clay or stone – usually with thatched roofs. Zulu and Tswana huts traditionally consisted of frameworks of sapling branches with conical thatched roofs.
Find examples of other indigenous dwellings. Paste or draw them in your workbook.
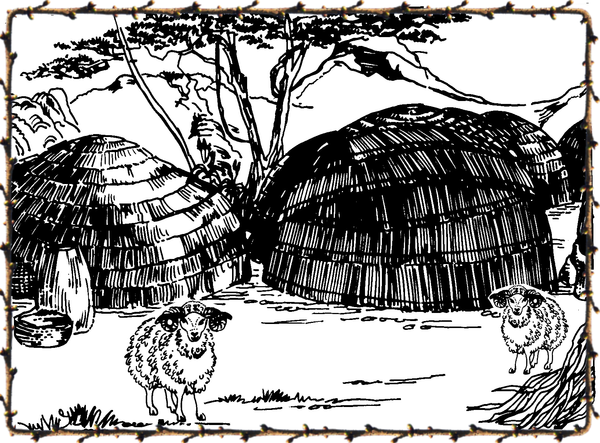

Zulu kraal
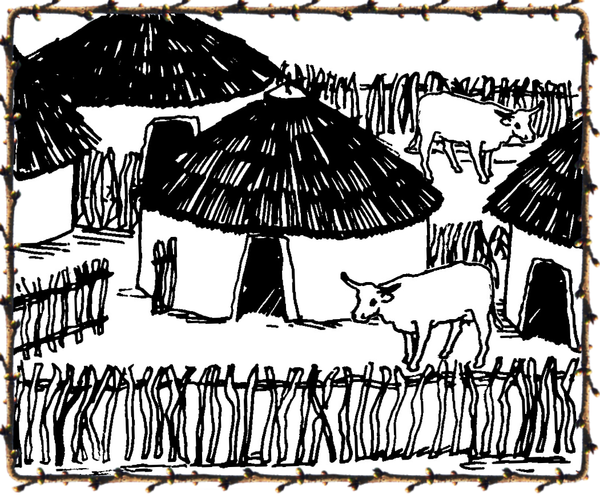

Nguni hut
e) Suppose that you are a spy who has to determine where the tribe's new kraal has to be built on behalf of your chief.
Draw a map of the countryside showing the ideal position for the new kraal. Then write a brief spying report (about five sentences) to persuade the chief to follow your suggestion for the location of the kraal. Provide reasons that refer to the veld, water and soil to justify your choice!
LEARNING OUTCOME 1: HISTORICAL ENQUIRY- The learner will be able to use enquiry skills to investigate the past and present
1.1 Access the sources
Start asking additional questions on events, artefacts, places, people. They vary in degree of difficulty.
1.2 Use the sources
Able to use page references
Know which sources (books) on specific topics contain information for an assignment / exhibition.
1.3 Communicate information from sources (reporting)
Able to explain information on a diagram, map, chart, sketch
Able to explain an event from the past orally or in writing.
Activity
a) hunter
b) reed mats
c) wind
e) the
f) livestock
g) round
h) were
i) when
j) supple, flexible
k) for
l) branches
m) it
n) reeds
o) into
p) this
q) in
b) The men hunted for meat, while the children cared for the livestock. The women were responsible for gathering berries and wild roots (veld food), and making clay pots for storing water and milk. Initially the Khoina was a race of shepherds along the coast of East Africa. Later they moved southwards after water and grazing. Since the tenth century they lived south of the Orange River.
The SAN were the first inhabitants of Southern Africa. The men were responsible for hunting and making arrows. The women gathered veld food, were responsible for the household, prepared food, cared for the children, and also built the shelters.
c) The kraal of the Khoina was built in the shape of a circle (beehive), surrounded by a hedge of thorn branches and poles for protection. The entrances to the huts all pointed to the inside of the kraal. At night the livestock slept in the middle of the kraal. The floors of the huts were smeared with manure, and the people slept on rush mats on the floor.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Social sciences: history grade 5' conversation and receive update notifications?