| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |

Through the work of scientists in the late 18th century, the main features of the electrostatic force —the existence of two types of charge, the observation that like charges repel, unlike charges attract, and the decrease of force with distance—were eventually refined, and expressed as a mathematical formula. The mathematical formula for the electrostatic force is called Coulomb’s law after the French physicist Charles Coulomb (1736–1806), who performed experiments and first proposed a formula to calculate it.
Coulomb’s law calculates the magnitude of the force between two point charges, and , separated by a distance . In SI units, the constant is equal to
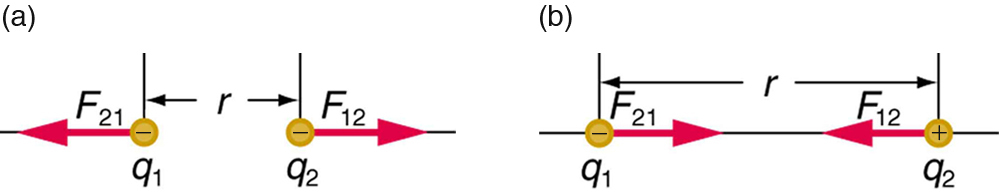
The electrostatic force is a vector quantity and is expressed in units of newtons. The force is understood to be along the line joining the two charges. (See [link] .)
Although the formula for Coulomb’s law is simple, it was no mean task to prove it. The experiments Coulomb did, with the primitive equipment then available, were difficult. Modern experiments have verified Coulomb’s law to great precision. For example, it has been shown that the force is inversely proportional to distance between two objects squared to an accuracy of 1 part in . No exceptions have ever been found, even at the small distances within the atom.
Compare the electrostatic force between an electron and proton separated by with the gravitational force between them. This distance is their average separation in a hydrogen atom.
Strategy
To compare the two forces, we first compute the electrostatic force using Coulomb’s law, . We then calculate the gravitational force using Newton’s universal law of gravitation. Finally, we take a ratio to see how the forces compare in magnitude.
Solution
Entering the given and known information about the charges and separation of the electron and proton into the expression of Coulomb’s law yields
Thus the Coulomb force is
The charges are opposite in sign, so this is an attractive force. This is a very large force for an electron—it would cause an acceleration of (verification is left as an end-of-section problem).The gravitational force is given by Newton’s law of gravitation as:
where . Here and represent the electron and proton masses, which can be found in the appendices. Entering values for the knowns yields
This is also an attractive force, although it is traditionally shown as positive since gravitational force is always attractive. The ratio of the magnitude of the electrostatic force to gravitational force in this case is, thus,
Discussion
This is a remarkably large ratio! Note that this will be the ratio of electrostatic force to gravitational force for an electron and a proton at any distance (taking the ratio before entering numerical values shows that the distance cancels). This ratio gives some indication of just how much larger the Coulomb force is than the gravitational force between two of the most common particles in nature.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Introductory physics - for kpu phys 1100 (2015 edition)' conversation and receive update notifications?