| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
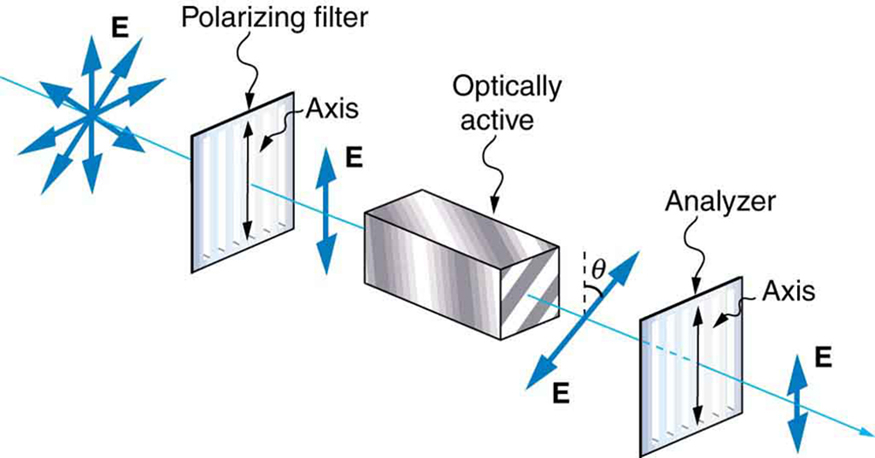
Many crystals and solutions rotate the plane of polarization of light passing through them. Such substances are said to be optically active . Examples include sugar water, insulin, and collagen (see [link] ). In addition to depending on the type of substance, the amount and direction of rotation depends on a number of factors. Among these is the concentration of the substance, the distance the light travels through it, and the wavelength of light. Optical activity is due to the asymmetric shape of molecules in the substance, such as being helical. Measurements of the rotation of polarized light passing through substances can thus be used to measure concentrations, a standard technique for sugars. It can also give information on the shapes of molecules, such as proteins, and factors that affect their shapes, such as temperature and pH.
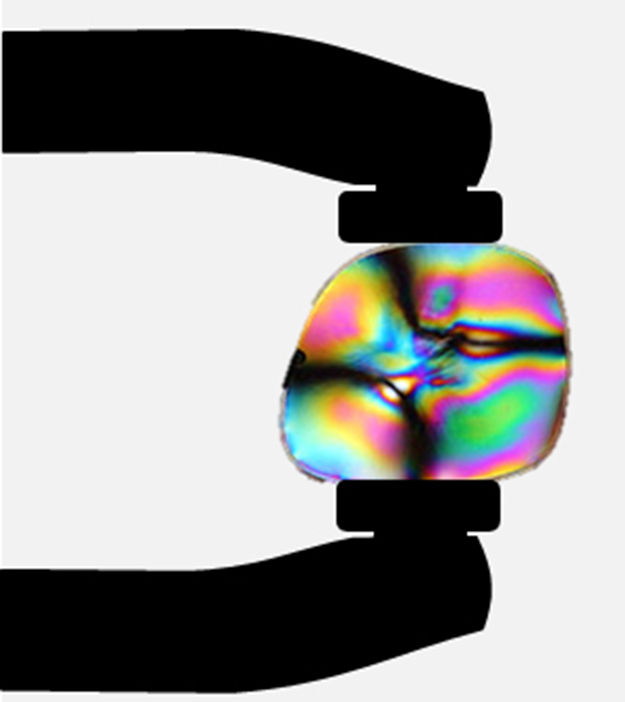
Glass and plastic become optically active when stressed; the greater the stress, the greater the effect. Optical stress analysis on complicated shapes can be performed by making plastic models of them and observing them through crossed filters, as seen in [link] . It is apparent that the effect depends on wavelength as well as stress. The wavelength dependence is sometimes also used for artistic purposes.
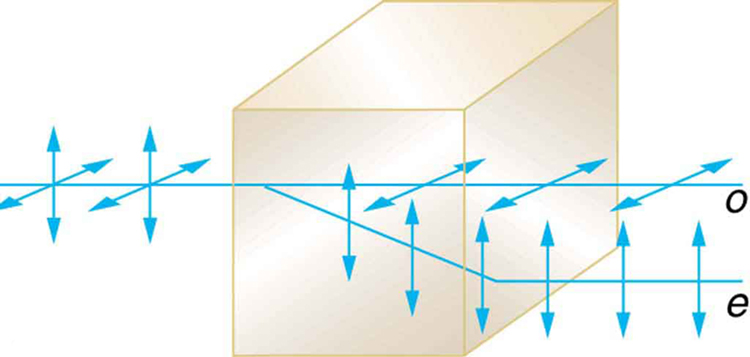
Another interesting phenomenon associated with polarized light is the ability of some crystals to split an unpolarized beam of light into two. Such crystals are said to be birefringent (see [link] ). Each of the separated rays has a specific polarization. One behaves normally and is called the ordinary ray, whereas the other does not obey Snell’s law and is called the extraordinary ray. Birefringent crystals can be used to produce polarized beams from unpolarized light. Some birefringent materials preferentially absorb one of the polarizations. These materials are called dichroic and can produce polarization by this preferential absorption. This is fundamentally how polarizing filters and other polarizers work. The interested reader is invited to further pursue the numerous properties of materials related to polarization.
Under what circumstances is the phase of light changed by reflection? Is the phase related to polarization?
Can a sound wave in air be polarized? Explain.
No light passes through two perfect polarizing filters with perpendicular axes. However, if a third polarizing filter is placed between the original two, some light can pass. Why is this? Under what circumstances does most of the light pass?
Explain what happens to the energy carried by light that it is dimmed by passing it through two crossed polarizing filters.
When particles scattering light are much smaller than its wavelength, the amount of scattering is proportional to . Does this mean there is more scattering for small than large ? How does this relate to the fact that the sky is blue?
Using the information given in the preceding question, explain why sunsets are red.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Concepts of physics' conversation and receive update notifications?