| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
So far we have discussed temperature change due to heat transfer. No temperature change occurs from heat transfer if ice melts and becomes liquid water (i.e., during a phase change). For example, consider water dripping from icicles melting on a roof warmed by the Sun. Conversely, water freezes in an ice tray cooled by lower-temperature surroundings.
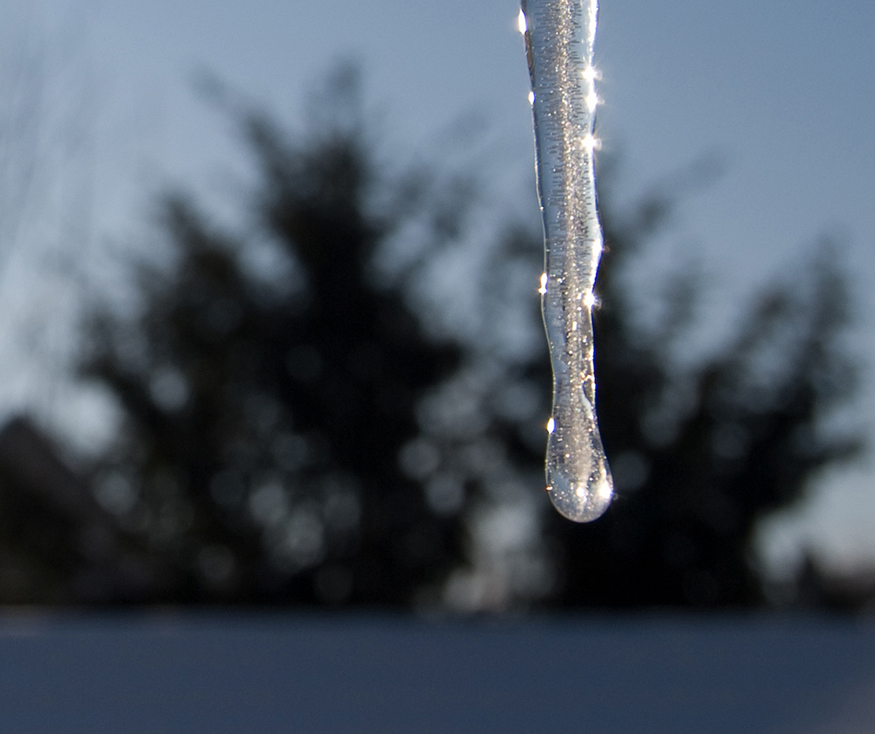

Energy is required to melt a solid because the cohesive bonds between the molecules in the solid must be broken apart such that, in the liquid, the molecules can move around at comparable kinetic energies; thus, there is no rise in temperature. Similarly, energy is needed to vaporize a liquid, because molecules in a liquid interact with each other via attractive forces. There is no temperature change until a phase change is complete. The temperature of a cup of soda initially at stays at until all the ice has melted. Conversely, energy is released during freezing and condensation, usually in the form of thermal energy. Work is done by cohesive forces when molecules are brought together. The corresponding energy must be given off (dissipated) to allow them to stay together [link] .
The energy involved in a phase change depends on two major factors: the number and strength of bonds or force pairs. The number of bonds is proportional to the number of molecules and thus to the mass of the sample. The strength of forces depends on the type of molecules. The heat required to change the phase of a sample of mass is given by
where the latent heat of fusion, , and latent heat of vaporization, , are material constants that are determined experimentally. See ( [link] ).
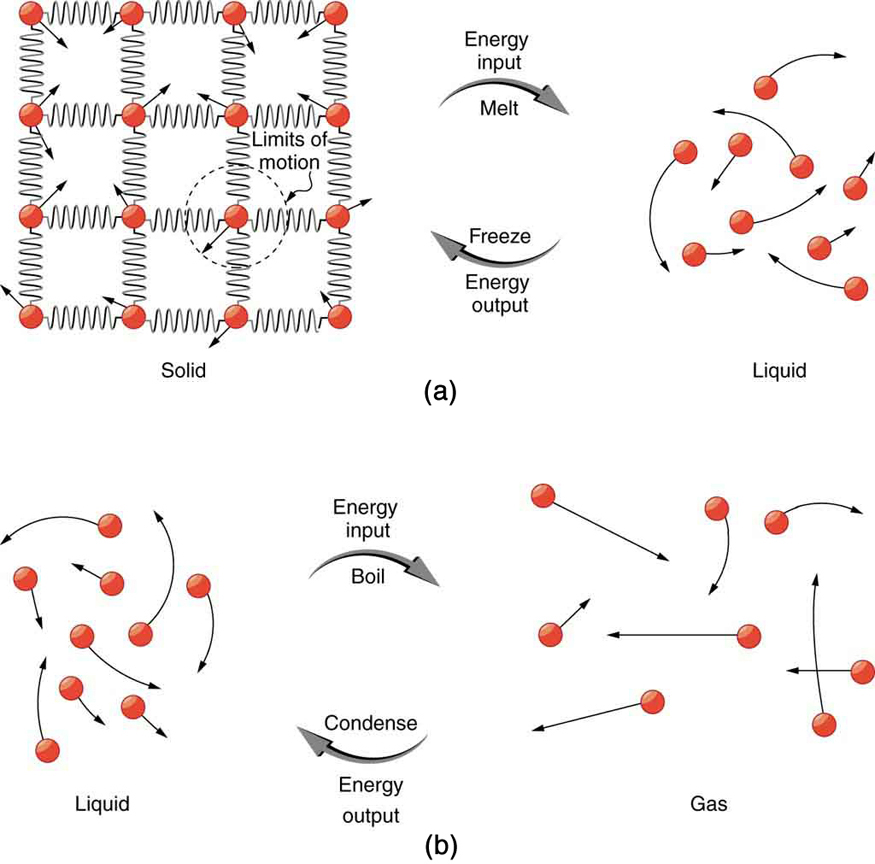
Latent heat is measured in units of J/kg. Both and depend on the substance, particularly on the strength of its molecular forces as noted earlier. and are collectively called latent heat coefficients . They are latent , or hidden, because in phase changes, energy enters or leaves a system without causing a temperature change in the system; so, in effect, the energy is hidden. [link] lists representative values of and , together with melting and boiling points.
The table shows that significant amounts of energy are involved in phase changes. Let us look, for example, at how much energy is needed to melt a kilogram of ice at to produce a kilogram of water at . Using the equation for a change in temperature and the value for water from [link] , we find that is the energy to melt a kilogram of ice. This is a lot of energy as it represents the same amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of 1 kg of liquid water from to . Even more energy is required to vaporize water; it would take 2256 kJ to change 1 kg of liquid water at the normal boiling point ( at atmospheric pressure) to steam (water vapor). This example shows that the energy for a phase change is enormous compared to energy associated with temperature changes without a phase change.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics ii' conversation and receive update notifications?