| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
For the figure below, we are given that .
Show that .
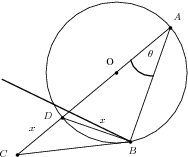
We want , and we have and . If we could get the angle , then we could use the cosine rule to determine . This is possible, as is a right-angled triangle. We know this from circle geometry, that any triangle circumscribed by a circle with one side going through the origin, is right-angled. As we have two angles of , we know and hence . Using the cosine rule, we can get .
Thus
Now the cosine rule gives
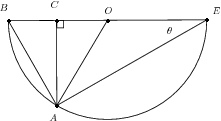
is the top of a tower of height . Its base is at . The triangle lies on the ground (a horizontal plane). If we have that , , and , show that
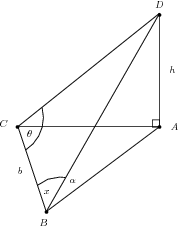
We have that the triangle is right-angled. Thus we can relate the height with the angle and either the length or (using sines or cosines). But we have two angles and a length for , and thus can work out all the remaining lengths and angles of this triangle. We can thus work out .
We have that
Now we need in terms of the given angles and length . Considering the triangle , we see that we can use the sine rule.
But , and
So
Taxicab geometry, considered by Hermann Minkowski in the 19th century, is a form of geometry in which the usual metric of Euclidean geometry is replaced by a new metric in which the distance between two points is the sum of the (absolute) differences of their coordinates.
The metric in taxi-cab geometry, is known as the Manhattan distance , between two points in an Euclidean space with fixed Cartesian coordinate system as the sum of the lengths of the projections of the line segment between the points onto the coordinate axes.
For example, the Manhattan distance between the point with coordinates and the point at is

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Siyavula textbooks: grade 12 maths' conversation and receive update notifications?