| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
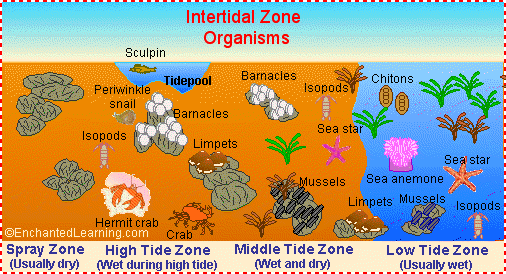
Figure Showing zonation
(Source from http://studentweb.cortland.edu/knowles86/Intertidalzone.gif )
Coral reefs are found in the warm, clear, shallow waters of tropical oceans around islands or along continental coastlines. They are mostly formed from calcium carbonateproduced by living coral. Reefs provide food and shelter for other organisms and protect shorelines from erosion.

Coral Reef. (Source: Coral Reef Alliance Photobank)
Estuaries are partially enclosed areas where fresh water and silt from streams or rivers mix with salty ocean water. They represent a transition from land to sea andfrom freshwater to saltwater. Estuaries are biologically very productive areas and provide homes for a wide variety of plants, birds and animals.
Terrestrial biomes characterise ecosystems on land, and are usually identified by the growth form of the dominant vegetation, climate, and/or where they are located on theearth. The major terrestrial biomes include the tundra biome , the forest biome , the grassland biome , and the desert biome . Note that forests and grasslands are defined based on the growth form of the dominant vegetation whereas deserts are classified based on the dominantclimatic conditions. The geographic distribution of terrestrial biomes is mostly influenced by climatic conditions such as rainfall and temperature. Themost recent classification of the biomes in South Africa divides the region into the following seven biomes:
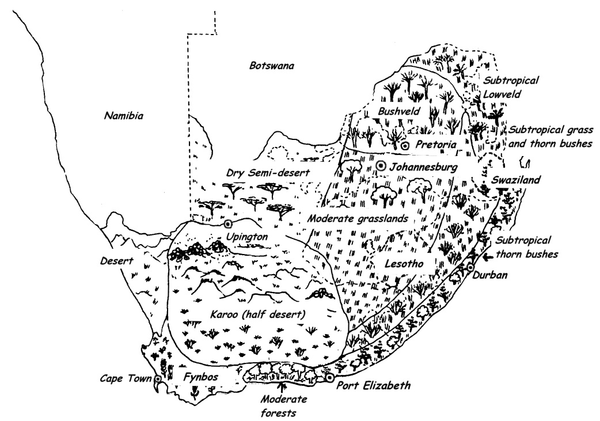
This map shows the different biomes of South Africa
(Source from http://cnx.org/content/m20153/latest/graphics1.png )
Grasslands cover regions where moderate rainfall is sufficient for the growth of grasses, but not enough for stands of trees. There are two main types ofgrasslands: tropical grasslands (savannas) and temperate grasslands . Tropical grasslands occur in warm climates such as Africa and very limited regions of Australia. They have a few scattered trees and shrubs, but theirdistinct rainy and dry seasons prevent the formation of tropical forests. Most temperate grasslands are treeless, relatively flat and have rich soil, havebeen replaced by farmland.

(Source from http://www.flickr.com/photos/takver/5884439290/sizes/o/in/photostream )
The information shown below shows the effect of climate change on the grassland biome
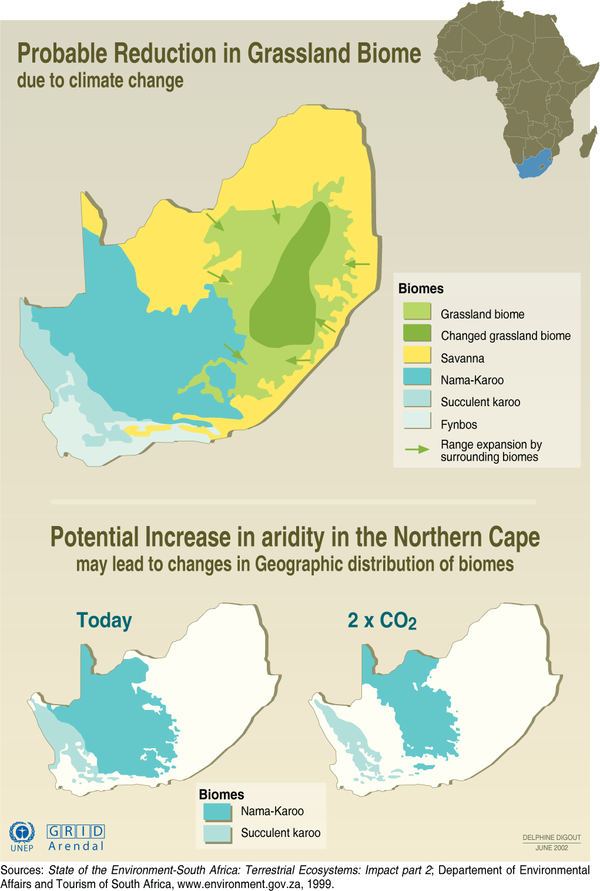
Figure Reduction in grassland biome
(Source from http://maps.grida.no/go/graphic/changing_biomes_in_south_africa )

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Siyavula: life sciences grade 10' conversation and receive update notifications?