| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Plasmids occur naturally in bacterial populations (such as Escherichia coli ) and have genes that can contribute favorable traits to the organism, such as antibiotic resistance (the ability to be unaffected by antibiotics). Plasmids have been highly engineered as vectors for molecular cloning and for the subsequent large-scale production of important molecules, such as insulin. A valuable characteristic of plasmid vectors is the ease with which a foreign DNA fragment can be introduced. These plasmid vectors contain many short DNA sequences that can be cut with different commonly available restriction enzymes . Restriction enzymes (also called restriction endonucleases) recognize specific DNA sequences and cut them in a predictable manner; they are naturally produced by bacteria as a defense mechanism against foreign DNA. Many restriction enzymes make staggered cuts in the two strands of DNA, such that the cut ends have a 2- to 4-nucleotide single-stranded overhang. The sequence that is recognized by the restriction enzyme is a four- to eight-nucleotide sequence that is a palindrome. Like with a word palindrome, this means the sequence reads the same forward and backward. In most cases, the sequence reads the same forward on one strand and backward on the complementary strand. When a staggered cut is made in a sequence like this, the overhangs are complementary ( [link] ).

Because these overhangs are capable of coming back together by hydrogen bonding with complementary overhangs on a piece of DNA cut with the same restriction enzyme, these are called “sticky ends.” The process of forming hydrogen bonds between complementary sequences on single strands to form double-stranded DNA is called annealing . Addition of an enzyme called DNA ligase, which takes part in DNA replication in cells, permanently joins the DNA fragments when the sticky ends come together. In this way, any DNA fragment can be spliced between the two ends of a plasmid DNA that has been cut with the same restriction enzyme ( [link] ).
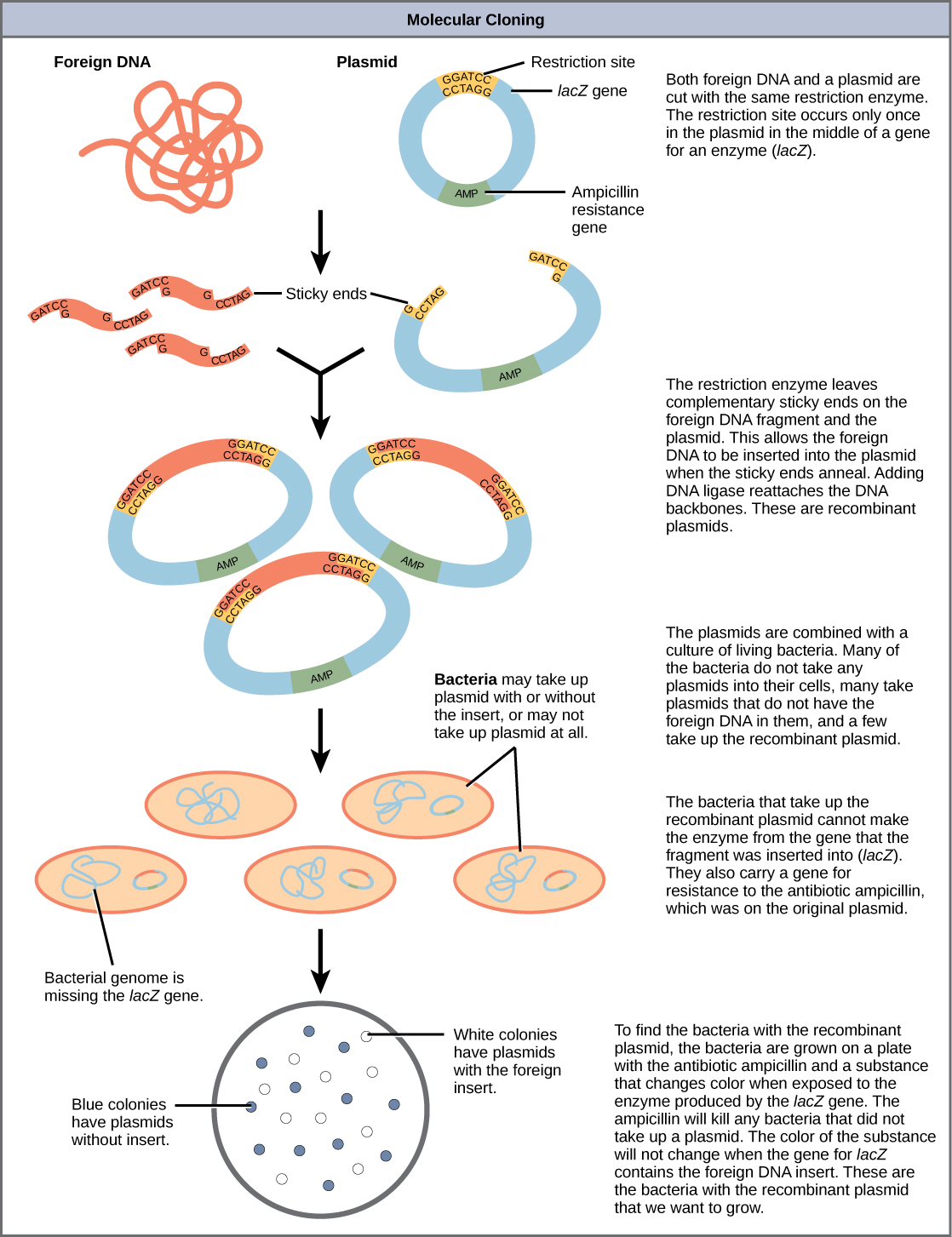
Plasmids with foreign DNA inserted into them are called recombinant DNA molecules because they contain new combinations of genetic material. Proteins that are produced from recombinant DNA molecules are called recombinant proteins . Not all recombinant plasmids are capable of expressing genes. Plasmids may also be engineered to express proteins only when stimulated by certain environmental factors, so that scientists can control the expression of the recombinant proteins.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Bmcc 101 - concepts of biology' conversation and receive update notifications?