| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Long-distance transmission over either kind of channel encounters attenuation problems. Losses in wireline channelsare explored in the Circuit Models module , where repeaters can extend the distance between transmitter and receiver beyond what passive losses thewireline channel imposes. In wireless channels, not only does radiation loss occur , but also one antenna may not "see" another because of the earth's curvature.
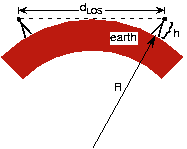
At the usual radio frequencies, propagating electromagnetic energy does not follow the earth's surface. Line-of-sight communication has the transmitter and receiver antennas in visual contact with each other. Assumingboth antennas have height above the earth's surface, maximum line-of-sight distance is
Derive the expression of line-of-sight distance using only the Pythagorean Theorem. Generalize it to the case where theantennas have different heights (as is the case with commercial radio and cellular telephone). What is the rangeof cellular telephone where the handset antenna has essentially zero height?
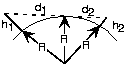
Use the Pythagorean Theorem, , where is the antenna height, is the distance from the top of the earth to a tangency point withthe earth's surface, and the earth's radius. The line-of-sight distance between twoearth-based antennae equals
Can you imagine a situation wherein global wireless communication is possible with only one transmittingantenna? In particular, what happens to wavelength when carrier frequency decreases?
As frequency decreases, wavelength increases and can approach the distance between the earth's surface and theionosphere. Assuming a distance between the two of 80 km, the relation gives a corresponding frequency of 3.75 kHz. Such low carrier frequencies would be limited to low bandwidth analogcommunication and to low datarate digital communications. The US Navy did use such a communicationscheme to reach all of its submarines at once.
Using a 100 m antenna would provide line-of-sight transmission over a distance of 71.4 km. Using such very tall antennas wouldprovide wireless communication within a town or between closely spaced population centers. Consequently, networks of antennas sprinkle the countryside (each located on the highest hill possible) to provide long-distance wirelesscommunications: Each antenna receives energy from one antenna and retransmits to another. This kind of network is known as a relay network .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Fundamentals of electrical engineering i' conversation and receive update notifications?