| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
As we have seen, any change in magnetic flux induces an emf opposing that change—a process known as induction. Motion is one of the major causes of induction. For example, a magnet moved toward a coil induces an emf, and a coil moved toward a magnet produces a similar emf. In this section, we concentrate on motion in a magnetic field that is stationary relative to the Earth, producing what is loosely called motional emf .
One situation where motional emf occurs is known as the Hall effect and has already been examined. Charges moving in a magnetic field experience the magnetic force , which moves opposite charges in opposite directions and produces an . We saw that the Hall effect has applications, including measurements of and . We will now see that the Hall effect is one aspect of the broader phenomenon of induction, and we will find that motional emf can be used as a power source.
Consider the situation shown in [link] . A rod is moved at a speed along a pair of conducting rails separated by a distance in a uniform magnetic field . The rails are stationary relative to and are connected to a stationary resistor . The resistor could be anything from a light bulb to a voltmeter. Consider the area enclosed by the moving rod, rails, and resistor. is perpendicular to this area, and the area is increasing as the rod moves. Thus the magnetic flux enclosed by the rails, rod, and resistor is increasing. When flux changes, an emf is induced according to Faraday’s law of induction.
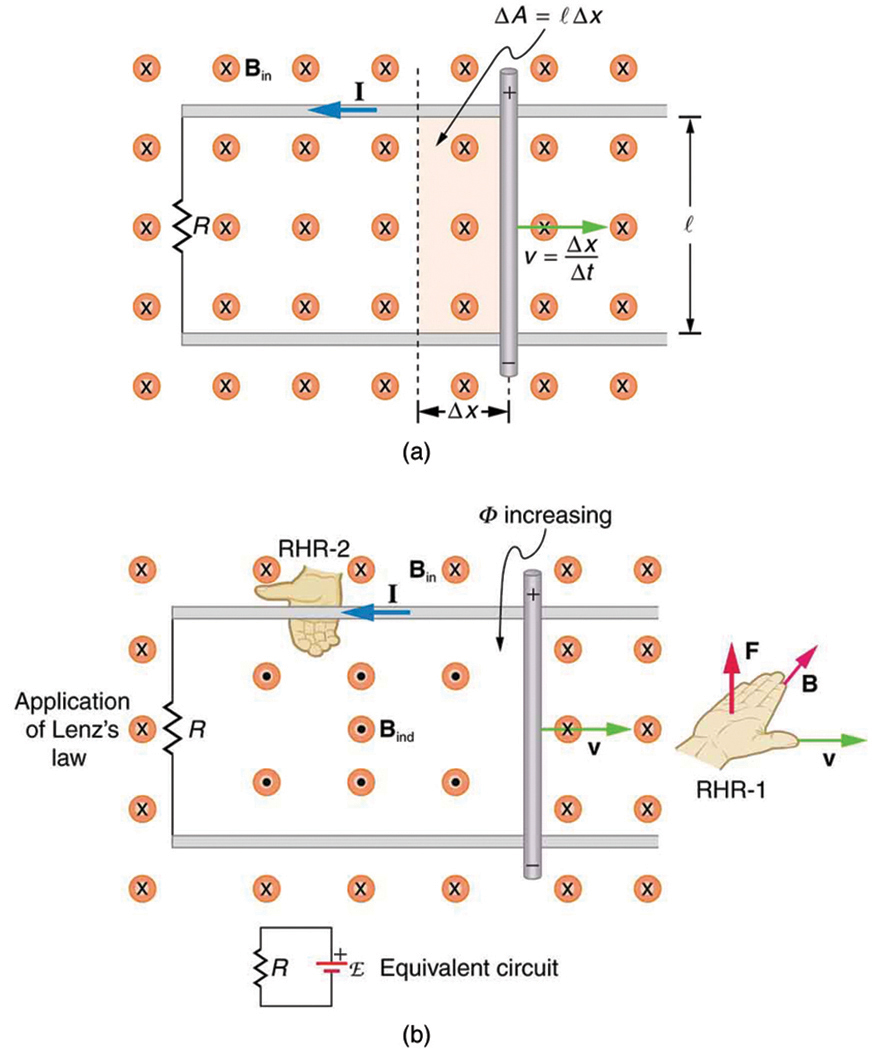
To find the magnitude of emf induced along the moving rod, we use Faraday’s law of induction without the sign:
Here and below, “emf” implies the magnitude of the emf. In this equation, and the flux . We have and , since is perpendicular to . Now , since is uniform. Note that the area swept out by the rod is . Entering these quantities into the expression for emf yields
Finally, note that , the velocity of the rod. Entering this into the last expression shows that
is the motional emf. This is the same expression given for the Hall effect previously.
There are many connections between the electric force and the magnetic force. The fact that a moving electric field produces a magnetic field and, conversely, a moving magnetic field produces an electric field is part of why electric and magnetic forces are now considered to be different manifestations of the same force. This classic unification of electric and magnetic forces into what is called the electromagnetic force is the inspiration for contemporary efforts to unify other basic forces.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics ii' conversation and receive update notifications?