| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
For the (7,4) example , we have error patterns that can be corrected. We start with single-bit error patterns, and multiply them by the parity check matrix.If we obtain unique answers, we are done; if two or more error patterns yield the same result, we can try double-bit errorpatterns. In our case, single-bit error patterns give a unique result.
| e | He |
|---|---|
| 1000000 | 101 |
| 0100000 | 111 |
| 0010000 | 110 |
| 0001000 | 011 |
| 0000100 | 100 |
| 0000010 | 010 |
| 0000001 | 001 |
This corresponds to our decoding table: We associate the parity check matrix multiplication result with the error pattern andadd this to the received word. If more than one error occurs (unlikely though it may be), this "error correction" strategyusually makes the error worse in the sense that more bits are changed from what was transmitted.
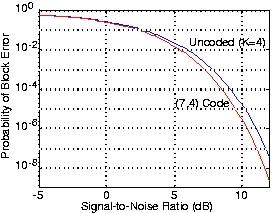
As with the repetition code, we must question whether our (7,4) code's error correction capability compensates for the increasederror probability due to the necessitated reduction in bit energy. [link] shows that if the signal-to-noise ratio is large enough channel coding yields asmaller error probability. Because the bit stream emerging from the source decoder is segmented into four-bit blocks, the fairway of comparing coded and uncoded transmission is to compute the probability of block error: the probability that any bit in a block remains in error despite errorcorrection and regardless of whether the error occurs in the data or in coding buts. Clearly, our (7,4) channel code doesyield smaller error rates, and is worth the additional systems required to make it work.
Note that our (7,4) code has the length and number of data bits that perfectly fits correcting single bit errors. This pleasantproperty arises because the number of error patterns that can be corrected, , equals the codeword length . Codes that have are known as Hamming codes , and the following table provides the parameters of these codes. Hamming codes are the simplest single-bit error correction codes, and thegenerator/parity check matrix formalism for channel coding and decoding works for them.
| (efficiency) | ||
|---|---|---|
| 3 | 1 | 0.33 |
| 7 | 4 | 0.57 |
| 15 | 11 | 0.73 |
| 31 | 26 | 0.84 |
| 63 | 57 | 0.90 |
| 127 | 120 | 0.94 |
Unfortunately, for such large blocks, the probability of multiple-bit errors can exceed the number of single-bit errorsunless the channel single-bit error probability is very small. Consequently, we need to enhance the code'serror correcting capability by adding double as well as single-bit error correction.
What must the relation between and be for a code to correct all single- and double-bit errors with a "perfect fit"?
In a length- block, single-bit and double-bit errors can occur. The number of non-zero vectors resulting from must equal or exceed the sum of these two numbers.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Fundamentals of electrical engineering i' conversation and receive update notifications?