| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
A quadrilateral is any polygon with four sides. The basic quadrilaterals are the trapezium, parallelogram, rectangle, rhombus, square and kite.
| Name of quadrilateral | Figure |
| trapezium | [link] |
| parallelogram | [link] |
| rectangle | [link] |
| rhombus | [link] |
| square | [link] |
| kite | [link] |
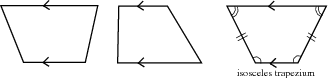
A trapezium is a quadrilateral with one pair of parallel opposite sides. It may also be called a trapezoid . A special type of trapezium is the isosceles trapezium , where one pair of opposite sides is parallel, the other pair of sides is equal in length and the angles at the ends of each parallel side are equal. An isosceles trapezium has one line of symmetry and its diagonals are equal in length.
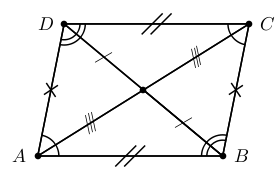
A trapezium with both sets of opposite sides parallel is called a parallelogram . A summary of the properties of a parallelogram is:
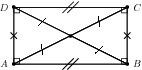
A rectangle is a parallelogram that has all four angles equal to . A summary of the properties of a rectangle is:
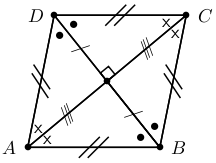
A rhombus is a parallelogram that has all four sides of equal length. A summary of the properties of a rhombus is:
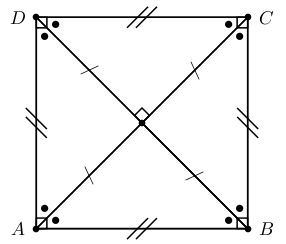
A square is a rhombus that has all four angles equal to 90 .
A summary of the properties of a square is:
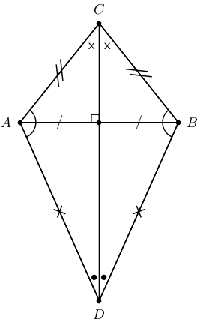
A kite is a quadrilateral with two pairs of adjacent sides equal.
A summary of the properties of a kite is:

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Siyavula textbooks: grade 10 maths [ncs]' conversation and receive update notifications?