| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
We know how to acquire analog signals for digital processing ( pre-filtering , sampling , and A/D conversion ) and to compute spectra of discrete-time signals (using the FFT algorithm ), let's put these various components together to learn how the spectrogram shown in [link] , which is used to analyze speech , is calculated. The speech was sampled at a rate of 11.025 kHzand passed through a 16-bit A/D converter.
Looking at [link] the signal lasted a little over 1.2 seconds. How long was thesampled signal (in terms of samples)? What was the datarate during the sampling process in bps (bits per second)?Assuming the computer storage is organized in terms of bytes (8-bit quantities), how many bytes of computer memory doesthe speech consume?
Number of samples equals . The datarate is kbps. The storage required would be bytes.
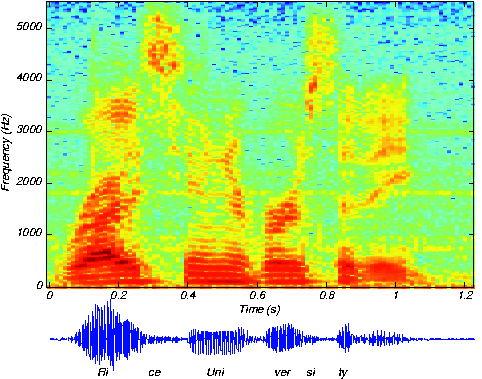
The resulting discrete-time signal, shown in the bottom of [link] , clearly changes its character with time. To display these spectral changes, thelong signal was sectioned into frames : comparatively short, contiguous groups of samples.Conceptually, a Fourier transform of each frame is calculated using the FFT. Each frame is not so long that significantsignal variations are retained within a frame, but not so short that we lose the signal's spectral character. Roughly speaking, the speech signal's spectrum is evaluated over successive time segments and stacked side by side so that the -axis corresponds to time and the -axis frequency, with color indicating the spectral amplitude.
An important detail emerges when we examine each framed signal
(
[link] ).
Spectrogram hanning vs. rectangular
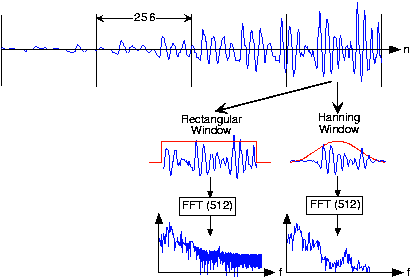
What might be the source of these oscillations? To gain some insight, what is thelength- discrete Fourier transform of a length- pulse? The pulse emulates the rectangular window, and certainly has edges.Compare your answer with the length- transform of alength- Hanning window.
The oscillations are due to the boxcar window's Fourier transform, which equals the sinc function.
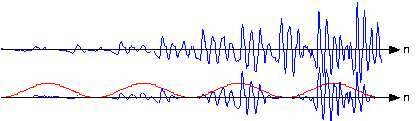
If you examine the windowed signal sections in sequence to examine windowing's effect on signal amplitude, we see that wehave managed to amplitude-modulate the signal with the periodically repeated window ( [link] ). To alleviate this problem, frames are overlapped (typically by half a frame duration). This solutionrequires more Fourier transform calculations than needed by rectangular windowing, but the spectra are much better behavedand spectral changes are much better captured.
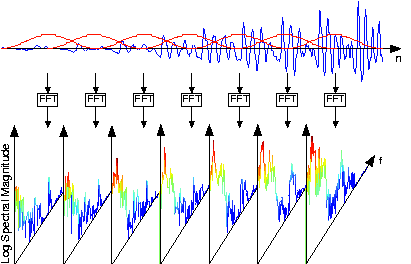
The speech signal, such as shown in the speech spectrogram , is sectioned into overlapping, equal-length frames, with a Hanning window appliedto each frame. The spectra of each of these is calculated, and displayed in spectrograms with frequency extending vertically,window time location running horizontally, and spectral magnitude color-coded. [link] illustrates these computations.
Why the specific values of 256 for and 512 for ? Another issue is how was the length-512 transform of each length-256 windowed framecomputed?
These numbers are powers-of-two, and the FFT algorithm can be exploited with these lengths. To compute a longertransform than the input signal's duration, we simply zero-pad the signal.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Fundamentals of electrical engineering i' conversation and receive update notifications?