| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In Double Integrals over Rectangular Regions , we studied the concept of double integrals and examined the tools needed to compute them. We learned techniques and properties to integrate functions of two variables over rectangular regions. We also discussed several applications, such as finding the volume bounded above by a function over a rectangular region, finding area by integration, and calculating the average value of a function of two variables.
In this section we consider double integrals of functions defined over a general bounded region on the plane. Most of the previous results hold in this situation as well, but some techniques need to be extended to cover this more general case.
An example of a general bounded region on a plane is shown in [link] . Since is bounded on the plane, there must exist a rectangular region on the same plane that encloses the region that is, a rectangular region exists such that is a subset of
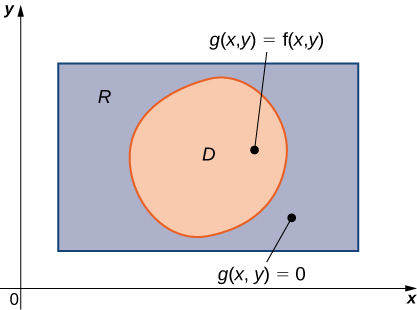
Suppose is defined on a general planar bounded region as in [link] . In order to develop double integrals of over we extend the definition of the function to include all points on the rectangular region and then use the concepts and tools from the preceding section. But how do we extend the definition of to include all the points on We do this by defining a new function on as follows:
Note that we might have some technical difficulties if the boundary of is complicated. So we assume the boundary to be a piecewise smooth and continuous simple closed curve. Also, since all the results developed in Double Integrals over Rectangular Regions used an integrable function we must be careful about and verify that is an integrable function over the rectangular region This happens as long as the region is bounded by simple closed curves. For now we will concentrate on the descriptions of the regions rather than the function and extend our theory appropriately for integration.
We consider two types of planar bounded regions.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Calculus volume 3' conversation and receive update notifications?