| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
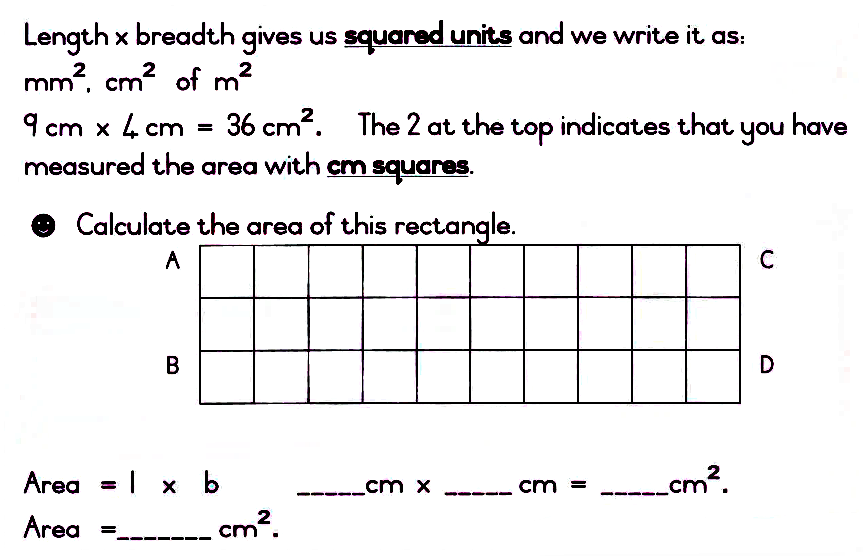
Number sentence: _____________________________________________________
You multiplied the length and the breath .
If I want to find out how big the space inside a rectangle is, I can say: length x breadth = space inside (area), therefore:
Area = l x b
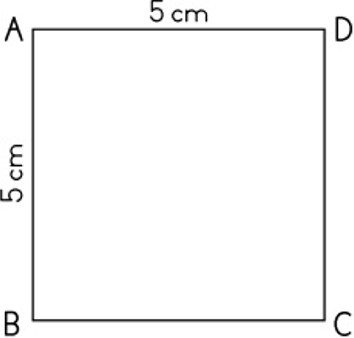
The length is 5 cm and the breadth is 5cm, therefore it is 5 cm x 5 cm = 25 cm².
Take 25 counters and make a square with them. Draw them. There are five rows of 5.
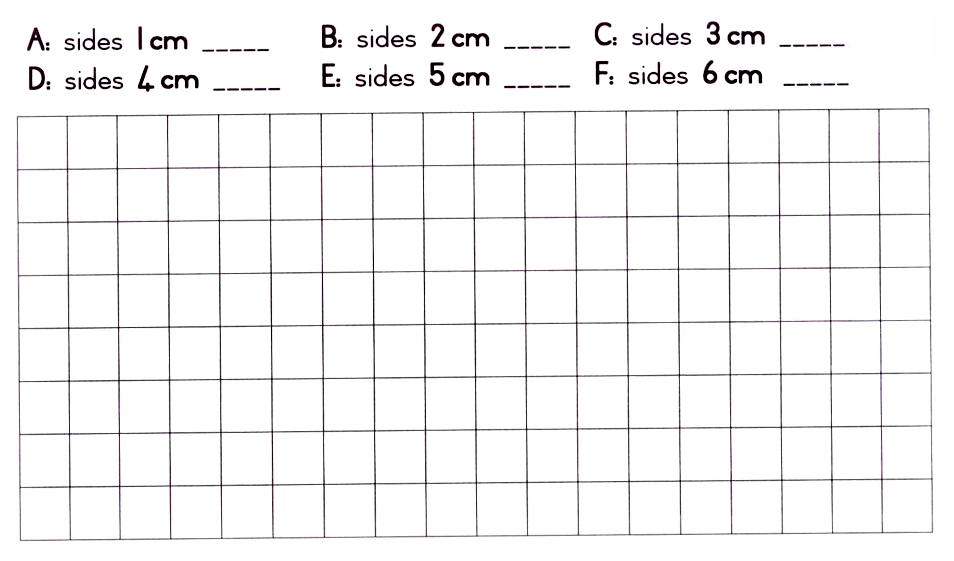
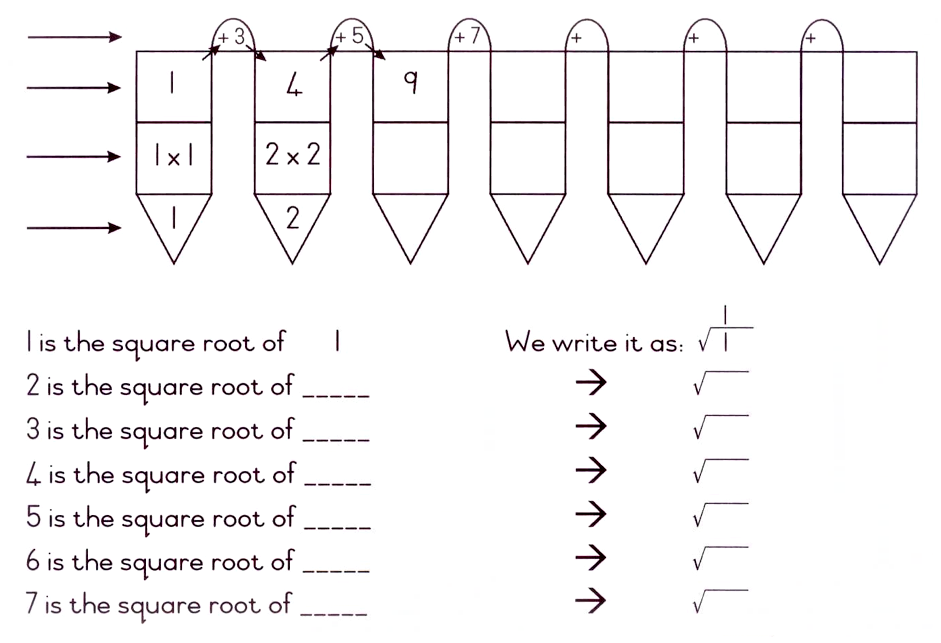
Because the length and the breadth are equal it is unnecessary to ask what the length and what the breadth is. Ask: What is the square root of 9? The square root of 9 is 3.
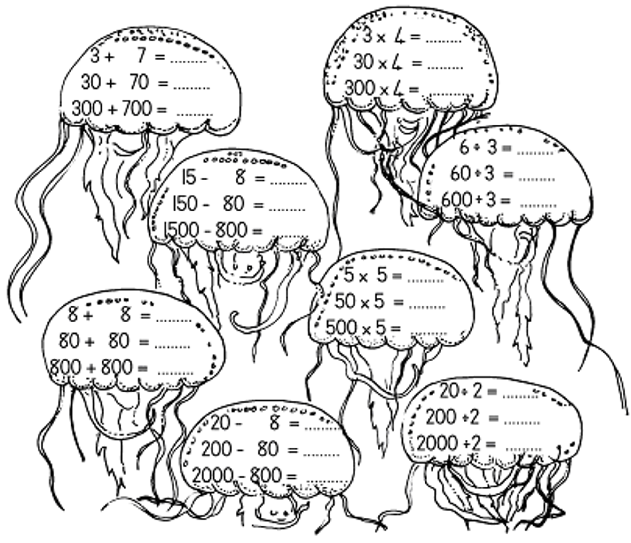
520 = _____ tens 790 = _____ tens
900 = _____ tens 1 000 = _____ tens
1 200 = _____ hundreds 1 500 = _____ honderde
1 900 = _____ hundreds 2 000 = _____ honderde
1 652 = _____ + _____ + _____ + _____
1 508 = _____ + _____ + _____ + _____
1 870 = _____ + _____ + _____ + _____
1 000 + 700 + 80 + 4 = ________
1 000 + 500 + 260 + 9 = ________
1 000 + 600 + 130 + 25 = ________
1 000 + 800 + 1 10 + 91 = ________
2 000 - 200 ...... 1 000 - 100 1504 + 20 ...... 1 304 + 200
1 450 + 130 ...... 1 680 - 100 1 280 + 40 ...... 1 280 + 400
1 446 : _______ 1 095 : _______ 1 901 : _______
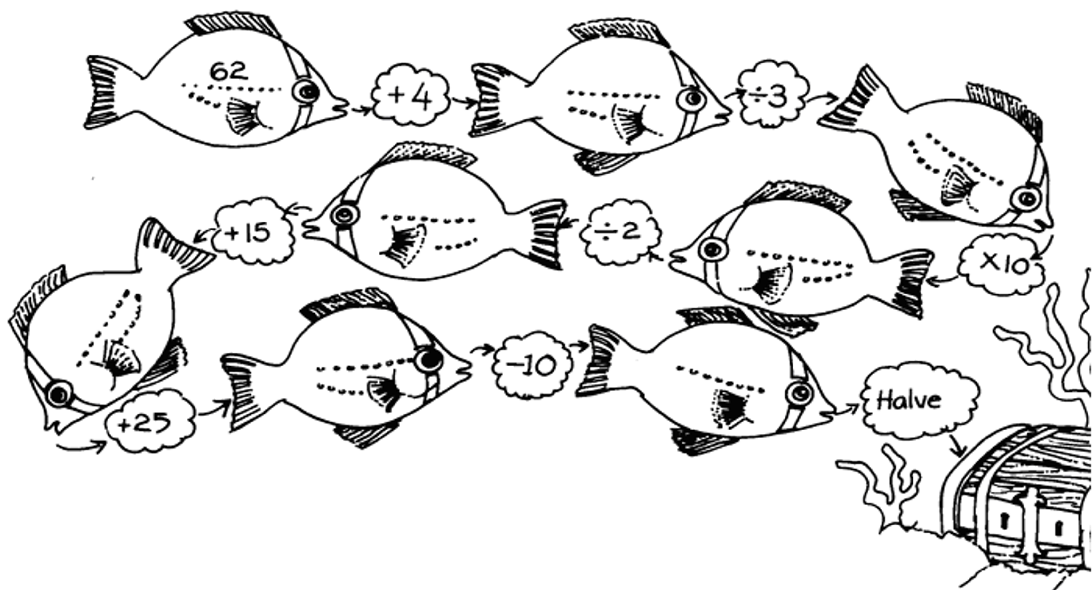
It has been a long year and your teacher is tired. Help her to mark the work.
1 332 is an even number.
2 195 is an even number.
1 998>1 989
1 824<1 842
1 000 + 300 + 63 = 1 336
1 643 = 1 000 + 500 + 143
1 505 comes just before 1 506
1 999 comes just before 1 998
566 doubled is 1 012
The halve of 1 840 is 920
2 x 349 = 698
624 ÷ 3 = 206
1 637 is 3 more than 1 640.
1 785 is 5 less than 1 790.
1 675 is halfway between 1 670 and 1 680.
| Mark the correct word with a : | True | False |
| A rectangle can have 3 right angles. | ||
| A sphere has the shape of a ball. | ||
| An isosceles triangle’s sides are all the same length. | ||
| A cool drink tin is cylindrical. | ||
| An egg is spherical. | ||
| A rectangle has 4 right angles. |
A (right angle / obtuse angle / acute angle) is 90° .
A cube has (4 / 6 / 8 ) faces.
An equilateral triangle has ( 1 / 2 / 3 ) sides that are equal.
167 + 205 + 99 =
750 - 145 - 260 =
34 x 3 - 57 =
255 - 191 ÷ 4 =

It is the last school day of the year.
Bonny and Tommy want to say good-bye because at 6:00 tomorrow morning they are leaving for Cape Town.
Learning Outcome 1: The learner will be able to recognise, describe and represent numbers and their relationships, and to count, estimate, calculate and check with competence and confidence in solving problems.
Assessment Standard 1.4: We know this when the learner orders, describes and compares numbers;
Assessment Standard 1.8: We know this when the learner can perform calculations, using appropriate symbols, to solve problems;
Assessment Standard 1.9: We know this when the learner performs mental calculations;
Assessment Standard 1.10: We know this when the learner uses the following techniques:
1.10.1 building up and breaking down numbers;
1.10.2 doubling and halving;
1.10.3 number-lines;
1.10.4 rounding off in tens.
Assessment Standard 1.12: We know this when the learner checks the solution given to problems by peers.
Learning Outcome 2: The learner will be able to recognise, describe and represent patterns and relationships, as well as to solve problems using algebraic language and skills.
Assessment Standard 2.2: We know this when the learner copies and extends simple number sequences to at least 1 000;
Assessment Standard 2.4: We know this when the learner describes observed patterns;
Learning Outcome 3: The learner will be able to describe and represent characteristics and relationships between two-dimensional shapes and three-dimensional objects in a variety of orientations and positions.
Assessment Standard 3.1: We know this when the learner recognises, identifies and names two-dimensional shapes and three-dimensional objects in the environment and in pictures,
Assessment Standard 3.5: We know this when the learner recognises and describes three-dimensional objects from different positions;
Learning Outcome 4: The learner will be able to use appropriate measuring units, instruments and formulae in a variety of contexts.
Assessment Standard 4.6: We know this when the learner investigates (alone and/or as a member of a group or team) and approximates.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Mathematics grade 3' conversation and receive update notifications?