| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Nitrosyl fluoride (ONF, molecular mass 49 amu) is a gas at room temperature. Water (H 2 O, molecular mass 18 amu) is a liquid, even though it has a lower molecular mass. We clearly cannot attribute this difference between the two compounds to dispersion forces. Both molecules have about the same shape and ONF is the heavier and larger molecule. It is, therefore, expected to experience more significant dispersion forces. Additionally, we cannot attribute this difference in boiling points to differences in the dipole moments of the molecules. Both molecules are polar and exhibit comparable dipole moments. The large difference between the boiling points is due to a particularly strong dipole-dipole attraction that may occur when a molecule contains a hydrogen atom bonded to a fluorine, oxygen, or nitrogen atom (the three most electronegative elements). The very large difference in electronegativity between the H atom (2.1) and the atom to which it is bonded (4.0 for an F atom, 3.5 for an O atom, or 3.0 for a N atom), combined with the very small size of a H atom and the relatively small sizes of F, O, or N atoms, leads to highly concentrated partial charges with these atoms. Molecules with F-H, O-H, or N-H moieties are very strongly attracted to similar moieties in nearby molecules, a particularly strong type of dipole-dipole attraction called hydrogen bonding . Examples of hydrogen bonds include HF⋯HF, H 2 O⋯HOH, and H 3 N⋯HNH 2 , in which the hydrogen bonds are denoted by dots. [link] illustrates hydrogen bonding between water molecules.
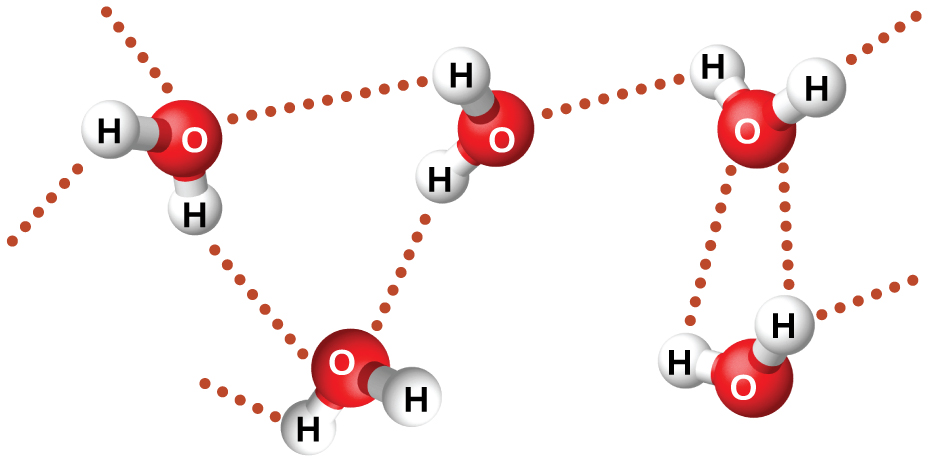
Despite use of the word “bond,” keep in mind that hydrogen bonds are intermolecular attractive forces, not intramolecular attractive forces (covalent bonds). Hydrogen bonds are much weaker than covalent bonds, only about 5 to 10% as strong, but are generally much stronger than other dipole-dipole attractions and dispersion forces.
Hydrogen bonds have a pronounced effect on the properties of condensed phases (liquids and solids). For example, consider the trends in boiling points for the binary hydrides of group 15 (NH 3 , PH 3 , AsH 3 , and SbH 3 ), group 16 hydrides (H 2 O, H 2 S, H 2 Se, and H 2 Te), and group 17 hydrides (HF, HCl, HBr, and HI). The boiling points of the heaviest three hydrides for each group are plotted in [link] . As we progress down any of these groups, the polarities of the molecules decrease slightly, whereas the sizes of the molecules increase substantially. The effect of increasingly stronger dispersion forces dominates that of increasingly weaker dipole-dipole attractions, and the boiling points are observed to increase steadily.
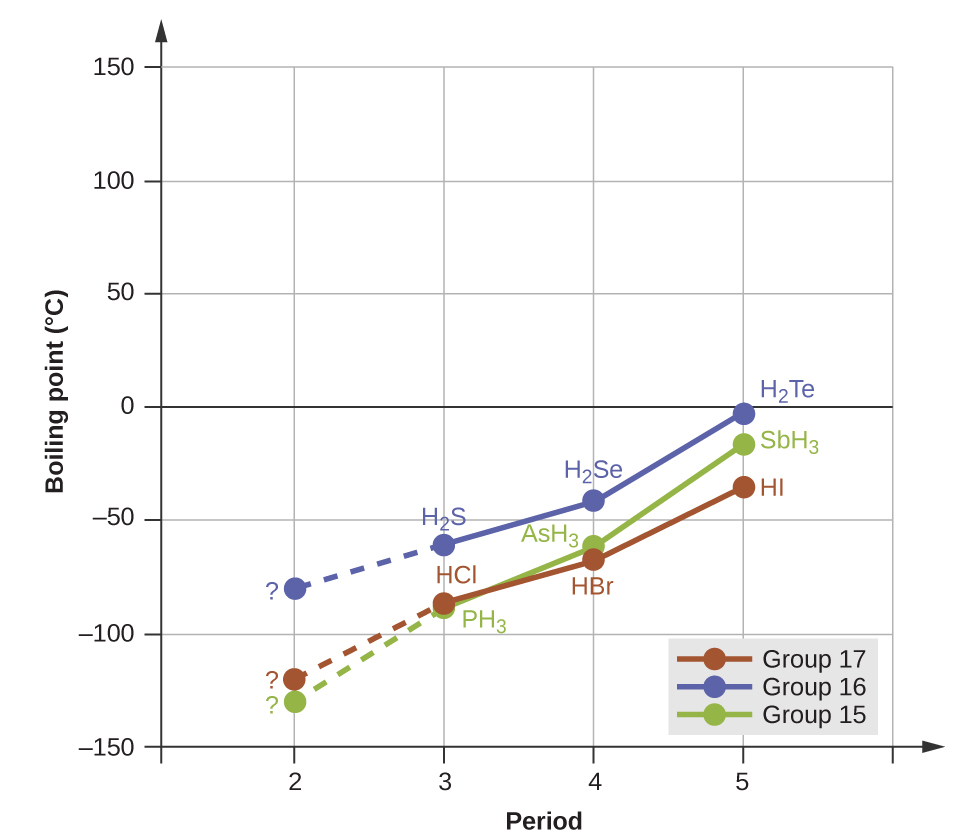
If we use this trend to predict the boiling points for the lightest hydride for each group, we would expect NH 3 to boil at about −120 °C, H 2 O to boil at about −80 °C, and HF to boil at about −110 °C. However, when we measure the boiling points for these compounds, we find that they are dramatically higher than the trends would predict, as shown in [link] . The stark contrast between our naïve predictions and reality provides compelling evidence for the strength of hydrogen bonding.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Ut austin - principles of chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?